Estrogen promotes breast cancer cell survival in an inhibitor of apoptosis (IAP)-dependent manner
- PMID: 21152357
- PMCID: PMC2996821
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-010-0018-6
Estrogen promotes breast cancer cell survival in an inhibitor of apoptosis (IAP)-dependent manner
Abstract
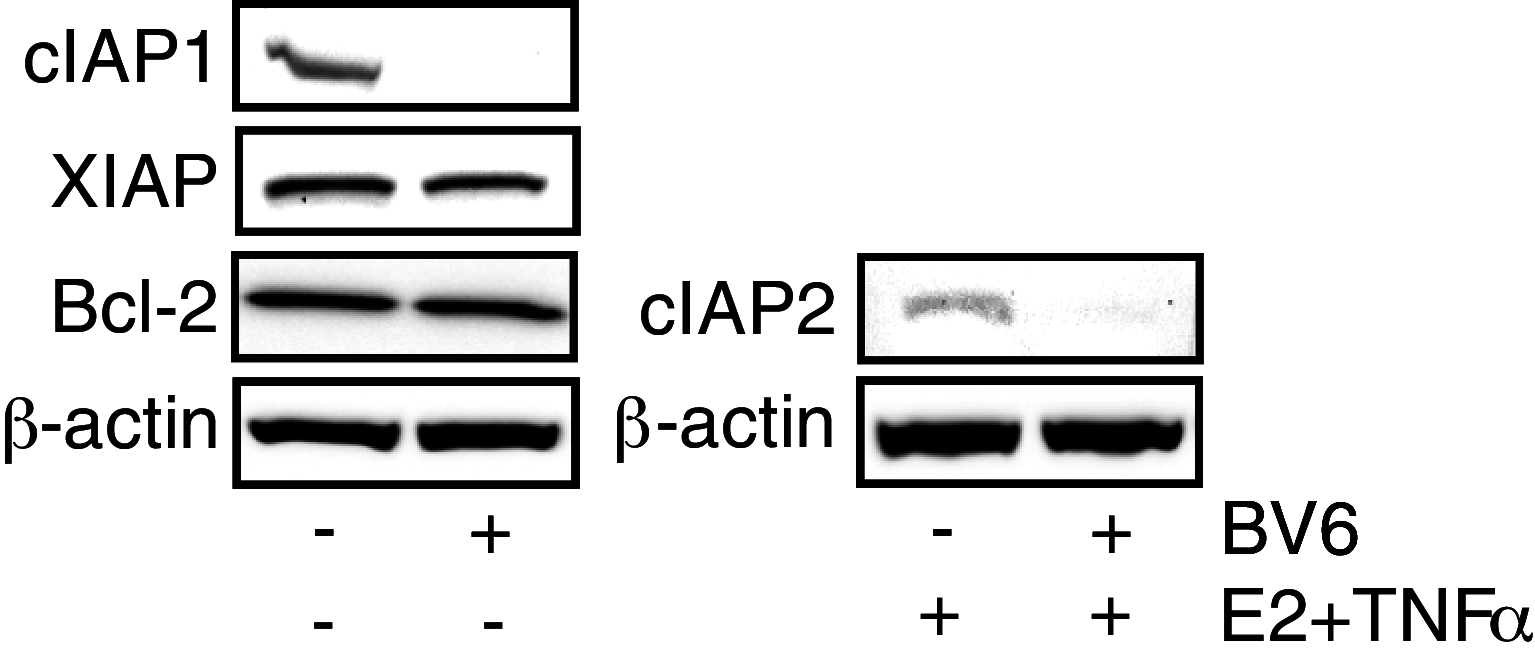
The estrogen receptor (ER) is a major prognostic and therapeutic marker that is expressed in nearly 75% of breast tumors. We have previously shown that the presence of inflammatory mediators can alter the genomic function of the estrogen receptor (ER) in a gene specific manner. In particular, 17β-estradiol (E2) works in combination with the pro-inflammatory cytokines to enhance the expression of a number of pro-survival factors, including the Inhibitor of Apoptosis (IAP) family member, cIAP2. Here we confirm that mRNA and protein levels for cIAP2, but not the related family members cIAP1 and XIAP, are highly up-regulated in MCF-7 breast cancer cells by E2 and cytokines. Similar regulation of cIAP2 is evident in other ER positive but not ER negative cell lines. In agreement with its role as a pro-survival factor, cIAP2 is highly expressed in a subset of invasive breast carcinomas but not in normal breast tissue or ductal carcinoma in situ. Antagonizing IAPs with mimetics of SMAC, which is a known endogenous IAP antagonist, or knockdown of IAPs by siRNA led to greater cell death by TNFα and prevented E2 from promoting cell survival. In addition, a SMAC mimetic reversed TNFα resistance in ER positive breast cancer cells that express high levels of endogenous IAPs. In summary, our findings indicate a new mechanism by which E2 allows breast cancer cells to evade cell death and suggest that an antagonist of IAPs may be a potential therapeutic option for a subset of ER positive breast tumors.
Keywords: Breast Cancer; Cell Survival; Cytokine; Estrogen; IAPs.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Inhibitor of Apoptosis Protein-1 Regulates Tumor Necrosis Factor-Mediated Destruction of Intestinal Epithelial Cells.Gastroenterology. 2017 Mar;152(4):867-879. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.11.019. Epub 2016 Nov 24. Gastroenterology. 2017. PMID: 27889570
-
Up-Regulation of Glioma-Associated Oncogene Homolog 1 Expression by Serum Starvation Promotes Cell Survival in ER-Positive Breast Cancer Cells.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;36(5):1862-76. doi: 10.1159/000430156. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015. PMID: 26182949
-
Targeting inhibitor of apoptosis proteins in combination with ErbB antagonists in breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res. 2009;11(3):R41. doi: 10.1186/bcr2328. Epub 2009 Jun 29. Breast Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19563669 Free PMC article.
-
Small-molecule SMAC mimetics as new cancer therapeutics.Pharmacol Ther. 2014 Oct;144(1):82-95. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2014.05.007. Epub 2014 May 16. Pharmacol Ther. 2014. PMID: 24841289 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Small Molecules Target Inhibitor of Apoptosis Proteins in Cancers with Deregulation of Extrinsic and Intrinsic Cell Death Pathways.Clin Cancer Res. 2017 Mar 15;23(6):1379-1387. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-2172. Epub 2016 Dec 30. Clin Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28039268 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The dual role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) in breast cancer: molecular insights and therapeutic approaches.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2020 Feb;43(1):1-18. doi: 10.1007/s13402-019-00489-1. Epub 2020 Jan 3. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2020. PMID: 31900901 Review.
-
Tumor Necrosis Factor α Blockade: An Opportunity to Tackle Breast Cancer.Front Oncol. 2020 Apr 22;10:584. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00584. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32391269 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The scaffold protein MEK Partner 1 is required for the survival of estrogen receptor positive breast cancer cells.Cell Commun Signal. 2012 Jul 9;10(1):18. doi: 10.1186/1478-811X-10-18. Cell Commun Signal. 2012. PMID: 22776333 Free PMC article.
-
An integrated bioinformatics approach identifies elevated cyclin E2 expression and E2F activity as distinct features of tamoxifen resistant breast tumors.PLoS One. 2011;6(7):e22274. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022274. Epub 2011 Jul 15. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21789246 Free PMC article.
-
CBP mediates NF-κB-dependent histone acetylation and estrogen receptor recruitment to an estrogen response element in the BIRC3 promoter.Mol Cell Biol. 2012 Jan;32(2):569-75. doi: 10.1128/MCB.05869-11. Epub 2011 Nov 14. Mol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22083956 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Teixeira C, Reed JC, Pratt MA. Estrogen promotes chemotherapeutic drug resistance by a mechanism involving Bcl-2 proto-oncogene expression in human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1995;55:3902–3907. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

