Initialization Parameter Sweep in ATHENA: Optimizing Neural Networks for Detecting Gene-Gene Interactions in the Presence of Small Main Effects
- PMID: 21152364
- PMCID: PMC2997651
- DOI: 10.1145/1830483.1830519
Initialization Parameter Sweep in ATHENA: Optimizing Neural Networks for Detecting Gene-Gene Interactions in the Presence of Small Main Effects
Abstract
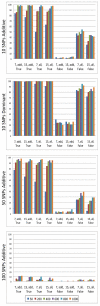
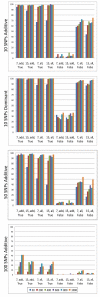
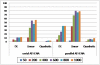
Recent advances in genotyping technology have led to the generation of an enormous quantity of genetic data. Traditional methods of statistical analysis have proved insufficient in extracting all of the information about the genetic components of common, complex human diseases. A contributing factor to the problem of analysis is that amongst the small main effects of each single gene on disease susceptibility, there are non-linear, gene-gene interactions that can be difficult for traditional, parametric analyses to detect. In addition, exhaustively searching all multi-locus combinations has proved computationally impractical. Novel strategies for analysis have been developed to address these issues. The Analysis Tool for Heritable and Environmental Network Associations (ATHENA) is an analytical tool that incorporates grammatical evolution neural networks (GENN) to detect interactions among genetic factors. Initial parameters define how the evolutionary process will be implemented. This research addresses how different parameter settings affect detection of disease models involving interactions. In the current study, we iterate over multiple parameter values to determine which combinations appear optimal for detecting interactions in simulated data for multiple genetic models. Our results indicate that the factors that have the greatest influence on detection are: input variable encoding, population size, and parallel computation.
Figures


References
-
- Bishop CM. Neural Networks for Pattern Recognition. Oxford University Press; London: 1995.
-
- Dudek SM, Motsinger AA, Velez DR, Williams SM, Ritchie MD. Data Simulation Software for Whole-Genome Association and Other Studies in Human Genetics. Pac Symp BioComput. 2006:499–510. - PubMed
-
- Edwards TL, Bush WS, Turner SD, Dudek SM, Torstenson ES, Schmidt M, Martin E, Ritchie MD. Generating Linkage Disequilibrium Patterns in Data Simulations Using genomeSIMLA. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. 2008;4793:24–35. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
