Molecular dynamics of ribosomal elongation factors G and Tu
- PMID: 21152913
- PMCID: PMC3045518
- DOI: 10.1007/s00249-010-0647-2
Molecular dynamics of ribosomal elongation factors G and Tu
Abstract
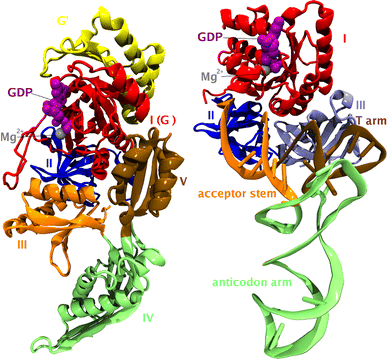
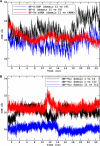
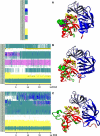
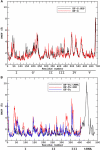
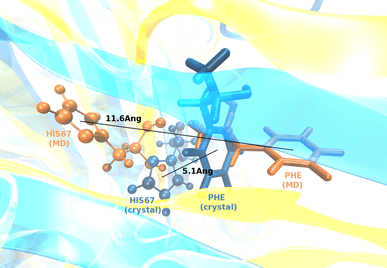
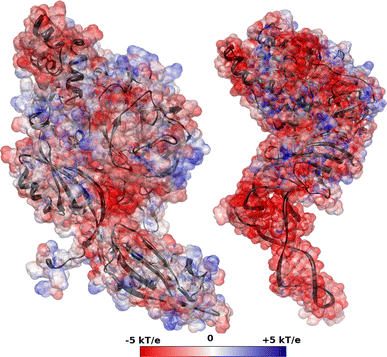
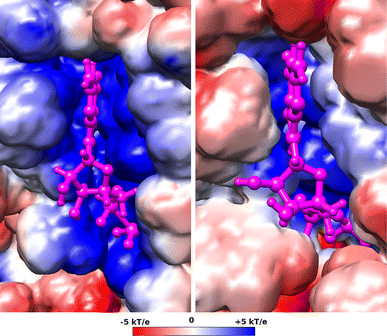
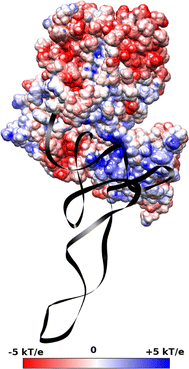
Translation on the ribosome is controlled by external factors. During polypeptide lengthening, elongation factors EF-Tu and EF-G consecutively interact with the bacterial ribosome. EF-Tu binds and delivers an aminoacyl-tRNA to the ribosomal A site and EF-G helps translocate the tRNAs between their binding sites after the peptide bond is formed. These processes occur at the expense of GTP. EF-Tu:tRNA and EF-G are of similar shape, share a common binding site, and undergo large conformational changes on interaction with the ribosome. To characterize the internal motion of these two elongation factors, we used 25 ns long all-atom molecular dynamics simulations. We observed enhanced mobility of EF-G domains III, IV, and V and of tRNA in the EF-Tu:tRNA complex. EF-Tu:GDP complex acquired a configuration different from that found in the crystal structure of EF-Tu with a GTP analogue, showing conformational changes in the switch I and II regions. The calculated electrostatic properties of elongation factors showed no global similarity even though matching electrostatic surface patches were found around the domain I that contacts the ribosome, and in the GDP/GTP binding region.
Figures
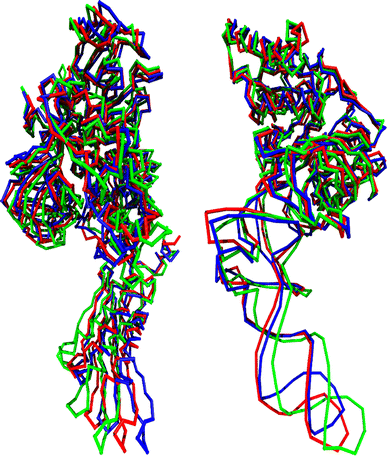

Similar articles
-
Mechanism of the chemical step for the guanosine triphosphate (GTP) hydrolysis catalyzed by elongation factor Tu.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008 Dec;1784(12):1908-17. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2008.08.003. Epub 2008 Aug 16. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008. PMID: 18773979 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of the ternary complex of Phe-tRNAPhe, EF-Tu, and a GTP analog.Science. 1995 Dec 1;270(5241):1464-72. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5241.1464. Science. 1995. PMID: 7491491
-
Structural dynamics of translation elongation factor Tu during aa-tRNA delivery to the ribosome.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Sep 19;46(16):8651-8661. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky651. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 30107527 Free PMC article.
-
Elongation in translation as a dynamic interaction among the ribosome, tRNA, and elongation factors EF-G and EF-Tu.Q Rev Biophys. 2009 Aug;42(3):159-200. doi: 10.1017/S0033583509990060. Q Rev Biophys. 2009. PMID: 20025795 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How can elongation factors EF-G and EF-Tu discriminate the functional state of the ribosome using the same binding site?FEBS Lett. 2005 Oct 24;579(25):5439-42. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2005.09.010. Epub 2005 Sep 26. FEBS Lett. 2005. PMID: 16213500 Review.
Cited by
-
Brownian dynamics study of the association between the 70S ribosome and elongation factor G.Biopolymers. 2011 Sep;95(9):616-27. doi: 10.1002/bip.21619. Epub 2011 Mar 10. Biopolymers. 2011. PMID: 21394717 Free PMC article.
-
Brucellosis in the omics era: integrative perspectives on Brucella genomic architecture, host-pathogen interactions, and disease dynamics.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025 Jul 11;41(7):264. doi: 10.1007/s11274-025-04484-7. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40640584 Review.
-
Elongation Factor Tu Switch I Element is a Gate for Aminoacyl-tRNA Selection.J Mol Biol. 2020 Apr 17;432(9):3064-3077. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2020.01.038. Epub 2020 Feb 13. J Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 32061931 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

