Gonadal steroids do not affect apolipoprotein E expression in aging mouse cerebral cortex
- PMID: 21152970
- PMCID: PMC11498561
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-010-9631-8
Gonadal steroids do not affect apolipoprotein E expression in aging mouse cerebral cortex
Abstract
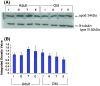
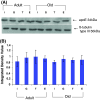
The allelic variant of apolipoprotein (Apo) E4 is a known risk factor for the development of most common late onset form of Alzheimer's disease (AD). As aging is associated with reduced circulating level of gonadal steroid hormones, hormone replacement therapies have been used for the possible treatment of AD. Both estrogen and testosterone have beneficial effects on brain due to interaction with apoE, but the underlying mechanism is still not clear. In this article, we report the effects of gonadectomy and hormone supplementation on apoE protein level in male and female mouse cerebral cortex during normal aging. We could not get any effect of gonadectomy and estradiol or testosterone treatment in adult and old mice of either sex. This suggests that during normal aging apoE protein level is not affected due to steroid hormone withdrawal or supplementation in the mouse cerebral cortex.
Figures
References
-
- Baum LW (2005) Sex, hormones, and Alzheimer’s disease. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 60:736–743 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

