Versatile TPR domains accommodate different modes of target protein recognition and function
- PMID: 21153002
- PMCID: PMC3118826
- DOI: 10.1007/s12192-010-0248-0
Versatile TPR domains accommodate different modes of target protein recognition and function
Abstract
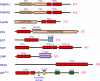
The tetratricopeptide repeat (TPR) motif is one of many repeat motifs that form structural domains in proteins that can act as interaction scaffolds in the formation of multi-protein complexes involved in numerous cellular processes such as transcription, the cell cycle, protein translocation, protein degradation and host defence against invading pathogens. The crystal structures of many TPR domain-containing proteins have been determined, showing TPR motifs as two anti-parallel α-helices packed in tandem arrays to form a structure with an amphipathic groove which can bind a target peptide. This is however not the only mode of target recognition by TPR domains, with short amino acid insertions and alternative TPR motif conformations also shown to contribute to protein interactions, highlighting diversity in TPR domains and the versatility of this structure in mediating biological events.
Figures
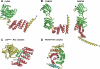
References
-
- Abo A, Pick E, Hall A, Totty N, Teahan CG, Segal AW. Activation of the NADPH oxidase involves the small GTP-binding protein p21rac1. Nature. 1991;353:668–670. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed S, Prigmore E, Govind S, Veryard C, Kozma R, Wientjes FB, Segal AW, Lim L. Cryptic Rac-binding and p21Cdc42HS/Rac-activated kinase phosphorylation sites of NADPH oxidase component p67phox. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:15693–15701. - PubMed
-
- Allan RK, Mok D, Ward BK, Ratajczak T. Modulation of chaperone function and cochaperone interaction by novobiocin in the C-terminal domain of Hsp90: evidence that coumarin antibiotics disrupt Hsp90 dimerization. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:7161–7171. - PubMed
-
- Andrade MA, Perez-Iratxeta C, Ponting CP. Protein repeats: structures, functions, and evolution. J Struct Biol. 2001;134:117–131. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

