A case report of Sandhoff disease
- PMID: 21153386
- PMCID: PMC3145082
- DOI: 10.1007/s00062-010-0035-4
A case report of Sandhoff disease
Abstract
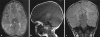
Sandhoff disease is a rare and severe lysosomal storage disorder representing 7% of GM2 gangliosidoses. Bilateral thalamic involvement has been suggested as a diagnostic marker of Sandhoff disease. A case of an 18-month-old infant admitted for psychomotor regression and drug resistant myoclonic epilepsy is presented. Cerebral CT scan showed bilateral and symmetrical thalamic hyperdensity. MRI revealed that the thalamus was hyperintense on T(1)-weighted images and hypointense on T2-weighted images with a hypersignal T2 of the white matter. Enzymatic assays objectified a deficiency of both hexosaminidases A and B confirming the diagnosis of Sandhoff disease.
References
-
- Gutierrez-Solana LG, Ruiz-Falco ML, Garcia-Penas JJ. Evolutive neuroradiological alterations in Sandhoff’s disease. Rev Neurol. 1996;24:1263–6. - PubMed
-
- Van der Knaap MS, Valk J, editors. Magnetic resonance of myelin, myelination, and myelin disorders. Berlin: Springer; 1995.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical