Immunoparalysis and nosocomial infection in children with multiple organ dysfunction syndrome
- PMID: 21153402
- PMCID: PMC5224706
- DOI: 10.1007/s00134-010-2088-x
Immunoparalysis and nosocomial infection in children with multiple organ dysfunction syndrome
Abstract
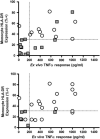
Purpose: Immunoparalysis defined by prolonged monocyte human leukocyte antigen DR depression is associated with adverse outcomes in adult severe sepsis and can be reversed with granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF). We hypothesized that immunoparalysis defined by whole-blood ex vivo lipopolysaccharide-induced tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNFα) response <200 pg/mL beyond day 3 of multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS) is similarly associated with nosocomial infection in children and can be reversed with GM-CSF.
Methods: In study period 1, we performed a multicenter cohort trial of transplant and nontransplant multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS) patients (≥2 organ failure). In study period 2, we performed an open-label randomized trial of GM-CSF therapy for nonneutropenic, nontransplant, severe MODS patients (≥3 organ failure) with TNFα response <160 pg/mL.
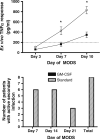
Results: Immunoparalysis was observed in 34% of MODS patients (n = 70) and was associated with increased nosocomial infection (relative risk [RR] 3.3, 95% confidence interval [1.8-6.0] p < 0.05) and mortality (RR 5.8 [2.1-16] p < 0.05). TNFα response <200 pg/mL throughout 7 days after positive culture was associated with persistent nosocomial infection, whereas recovery above 200 pg/mL was associated with resolution of infection (p < 0.05). In study period 2, GM-CSF therapy facilitated rapid recovery of TNFα response to >200 pg/mL by 7 days (p < 0.05) and prevented nosocomial infection (no infections in seven patients versus eight infections in seven patients) (p < 0.05).
Conclusions: Similar to in adults, immunoparalysis is a potentially reversible risk factor for development of nosocomial infection in pediatric MODS. Whole-blood ex vivo TNFα response is a promising biomarker for monitoring this condition.
Figures
References
-
- Leclerc F, Leteurtre S, Duhamel A, Grandbastien B, Proulx F, Martinot A, Gauvin F, Hubert P, Lacroix J. Cumulative influence of organ dysfunctions and septic state on mortality of critically ill children. Am J Resp Crit Care Med. 2005;171:348–353. - PubMed
-
- Pizzo PA, Rubin M, Freifeld A, Walsh TJ. The child with cancer and infection. I. Empiric therapy for fever and neutropenia, and preventive strategies. J Pediatr. 1991;119:679–694. - PubMed
-
- Felmet KA, Hall MW, Clark RS, Jaffe R, Carcillo JA. Prolonged lymphopenia, lymphoid depletion, and hypoprolactinemia in children with nosocomial sepsis and multiple organ failure. J Immunol. 2005;174:3765–3772. - PubMed
-
- Hoffman JA, Weinberg KI, Azen CG, Horn MV, Dukes L, Starnes VA, Woo MS. Human leukocyte antigen-DR expression on peripheral blood monocytes and the risk of pneumonia in pediatric lung transplant recipients. Transpl Infect Dis. 2004;6:147–155. - PubMed
-
- Volk HD, Reinke P, Krausch D, Zuckermann H, Asadullah K, Muller JM, Docke WD, Kox WJ. Monocyte deactivation–rationale for a new therapeutic strategy in sepsis. Intensive Care Med. 1996;22(Suppl 4):S474–S481. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

