EicosaCell - an immunofluorescent-based assay to localize newly synthesized eicosanoid lipid mediators at intracellular sites
- PMID: 21153792
- PMCID: PMC3679533
- DOI: 10.1007/978-1-60761-950-5_10
EicosaCell - an immunofluorescent-based assay to localize newly synthesized eicosanoid lipid mediators at intracellular sites
Abstract
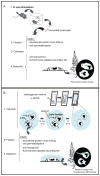
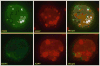
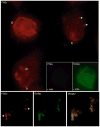
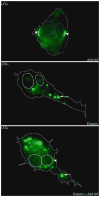
Eicosanoids (prostaglandins, leukotrienes and lipoxins) are a family of signaling lipids derived from arachidonic acid that have important roles in physiological and pathological processes. Over the past years, it has been established that successful eicosanoid production is not merely determined by arachidonic acid and eicosanoid-forming enzymes availability, but requires sequential interactions between specific biosynthetic proteins acting in cascade and may involve very unique spatial interactions. Direct assessment of specific subcellular locales of eicosanoid synthesis has been elusive, as those lipid mediators are newly formed, not stored and often rapidly released upon cell stimulation. In this chapter, we discuss the EicosaCell protocol for intracellular detection of eicosanoid-synthesizing compartments by means of a strategy to covalently cross-link and immobilize the lipid mediators at their sites of synthesis followed by immunofluorescent-based localization of the targeted eicosanoid.
Figures

References
-
- Yaqoob P. Fatty acids as gatekeepers of immune cell regulation. Trends Immunol. 2003;24:639–645. - PubMed
-
- Wymann MP, Schneiter R. Lipid signaling in disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008;9:162–176. - PubMed
-
- Smith WL, DeWitt DL, Garavito RM. Cyclooxygenases: structural, cellular, and molecular biology. Annu Rev Biochem. 2000;69:145–182. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

