Computerized analysis of pneumoconiosis in digital chest radiography: effect of artificial neural network trained with power spectra
- PMID: 21153856
- PMCID: PMC3222544
- DOI: 10.1007/s10278-010-9357-7
Computerized analysis of pneumoconiosis in digital chest radiography: effect of artificial neural network trained with power spectra
Abstract
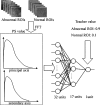
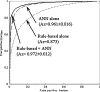
It is difficult for radiologists to classify pneumoconiosis with small nodules on chest radiographs. Therefore, we have developed a computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) system based on the rule-based plus artificial neural network (ANN) method for distinction between normal and abnormal regions of interest (ROIs) selected from chest radiographs with and without pneumoconiosis. The image database consists of 11 normal and 12 abnormal chest radiographs. These abnormal cases included five silicoses, four asbestoses, and three other pneumoconioses. ROIs (matrix size, 32 × 32) were selected from normal and abnormal lungs. We obtained power spectra (PS) by Fourier transform for the frequency analysis. A rule-based method using PS values at 0.179 and 0.357 cycles per millimeter, corresponding to the spatial frequencies of nodular patterns, were employed for identification of obviously normal or obviously abnormal ROIs. Then, ANN was applied for classification of the remaining normal and abnormal ROIs, which were not classified as obviously abnormal or normal by the rule-based method. The classification performance was evaluated by the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (Az value). The Az value was 0.972 ± 0.012 for the rule-based plus ANN method, which was larger than that of 0.961 ± 0.016 for the ANN method alone (P ≤ 0.15) and that of 0.873 for the rule-based method alone. We have developed a rule-based plus pattern recognition technique based on the ANN for classification of pneumoconiosis on chest radiography. Our CAD system based on PS would be useful to assist radiologists in the classification of pneumoconiosis.
Figures




References
-
- Guidelines for the use ILO international classification of radiographs of pneumoconiosis. Genva: ILO; 1980. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

