Activity-dependent changes in the firing properties of neocortical fast-spiking interneurons in the absence of large changes in gene expression
- PMID: 21154910
- PMCID: PMC3059083
- DOI: 10.1002/dneu.20811
Activity-dependent changes in the firing properties of neocortical fast-spiking interneurons in the absence of large changes in gene expression
Abstract
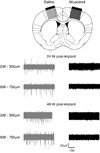
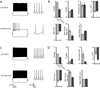
The diverse cell types that comprise neocortical circuits each have characteristic integrative and firing properties that are specialized to perform specific functions within the network. Parvalbumin-positive fast-spiking (FS) interneurons are a particularly specialized cortical cell-type that controls the dynamics of ongoing activity and prevents runaway excitation by virtue of remarkably high firing rates, a feature that is permitted by narrow action potentials and the absence of spike-frequency adaptation. Although several neuronal intrinsic membrane properties undergo activity-dependent plasticity, the role of network activity in shaping and maintaining specialized, cell-type-specific firing properties is unknown. We tested whether the specialized firing properties of mature FS interneurons are sensitive to activity perturbations by inactivating a portion of motor cortex in vivo for 48 h and measuring resulting plasticity of FS intrinsic and firing properties with whole-cell recording in acute slices. Many of the characteristic properties of FS interneurons, including nonadapting high-frequency spiking and narrow action potentials, were profoundly affected by activity deprivation both at an age just after maturation of FS firing properties and also a week after their maturation. Using microarray screening, we determined that although normal maturation of FS electrophysiological specializations is accompanied by large-scale transcriptional changes, the effects of deprivation on the same specializations involve more modest transcriptional changes, and may instead be primarily mediated by post-transcriptional mechanisms.
Copyright © 2010 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Arlotta P, Molyneaux BJ, Chen J, Inoue J, Kominami R, Macklis JD. Neuronal subtype-specific genes that control corticospinal motor neuron development in vivo. Neuron. 2005;45:207–221. - PubMed
-
- Butt SJ, Fuccillo M, Nery S, Noctor S, Kriegstein A, Corbin JG, Fishell G. The temporal and spatial origins of cortical interneurons predict their physiological subtype. Neuron. 2005;48:591–604. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

