Inhibitor and activator: dual functions for SHIP in immunity and cancer
- PMID: 21155837
- PMCID: PMC4515353
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2010.05869.x
Inhibitor and activator: dual functions for SHIP in immunity and cancer
Abstract
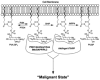
SHIP1 is at the nexus of intracellular signaling pathways in immune cells that mediate bone marrow (BM) graft rejection, production of inflammatory and immunosuppressive cytokines, immunoregulatory cell formation, the BM niche that supports development of the immune system, and immune cancers. This review summarizes how SHIP participates in normal immune physiology or the pathologies that result when SHIP is mutated. This review also proposes that SHIP can have either inhibitory or activating roles in cell signaling that are determined by whether signaling pathways distal to PI3K are promoted by SHIP's substrate (PI(3,4,5)P(3) ) or its product (PI(3,4)P(2) ). This review also proposes the "two PIP hypothesis" that postulates that both SHIP's product and its substrate are necessary for a cancer cell to achieve and sustain a malignant state. Finally, due to the recent discovery of small molecule antagonists and agonists for SHIP, this review discusses potential therapeutic settings where chemical modulation of SHIP might be of benefit.
© 2010 New York Academy of Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
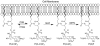

References
-
- Kavanaugh WM, Pot DA, Chin SM, Deuter-Reinhard M, Jefferson AB, Norris FA, Masiarz FR, Cousens LS, Majerus PW, Williams LT. Multiple forms of an inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase form signaling complexes with Shc and Grb2. Current Biology. 1996;6:438–445. - PubMed
-
- Damen JE, Liu L, Rosten P, Humphries RK, Jefferson AB, Majerus PW, Krystal G. The 145-kDa protein induced to associate with Shc by multiple cytokines is an inositol tetraphosphate and phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-triphosphate 5-phosphatase. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1996;93:1689–1693. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lioubin MN, Algate PA, Tsai S, Carlberg K, Aebersold A, Rohrschneider LR. p150Ship, a signal transduction molecule with inositol polyphosphate-5-phosphatase activity. Genes & Development. 1996;10:1084–1095. - PubMed
-
- Hawkins PT, A K, Davidson K, Stephens LR. Signalling through Class I PI3Ks in mammalian cells. Biochem Soc Trans. 2006;34(Pt 5):647–662. - PubMed
-
- Xia HJ, Yang G. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate 3-kinases: functions and regulations. Cell Res. 2005;15:83–91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

