Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II inhibitors disrupt AKAP79-dependent PKC signaling to GluA1 AMPA receptors
- PMID: 21156788
- PMCID: PMC3057809
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.183558
Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II inhibitors disrupt AKAP79-dependent PKC signaling to GluA1 AMPA receptors
Abstract
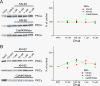
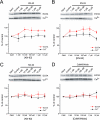
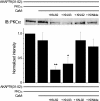
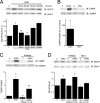
GluA1 (formerly GluR1) AMPA receptor subunit phosphorylation at Ser-831 is an early biochemical marker for long-term potentiation and learning. This site is a substrate for Ca(2+)/calmodulin (CaM)-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) and protein kinase C (PKC). By directing PKC to GluA1, A-kinase anchoring protein 79 (AKAP79) facilitates Ser-831 phosphorylation and makes PKC a more potent regulator of GluA1 than CaMKII. PKC and CaM bind to residues 31-52 of AKAP79 in a competitive manner. Here, we demonstrate that common CaMKII inhibitors alter PKC and CaM interactions with AKAP79(31-52). Most notably, the classical CaMKII inhibitors KN-93 and KN-62 potently enhanced the association of CaM to AKAP79(31-52) in the absence (apoCaM) but not the presence of Ca(2+). In contrast, apoCaM association to AKAP79(31-52) was unaffected by the control compound KN-92 or a mechanistically distinct CaMKII inhibitor (CaMKIINtide). In vitro studies demonstrated that KN-62 and KN-93, but not the other compounds, led to apoCaM-dependent displacement of PKC from AKAP79(31-52). In the absence of CaMKII activation, complementary cellular studies revealed that KN-62 and KN-93, but not KN-92 or CaMKIINtide, inhibited PKC-mediated phosphorylation of GluA1 in hippocampal neurons as well as AKAP79-dependent PKC-mediated augmentation of recombinant GluA1 currents. Buffering cellular CaM attenuated the ability of KN-62 and KN-93 to inhibit AKAP79-anchored PKC regulation of GluA1. Therefore, by favoring apoCaM binding to AKAP79, KN-62 and KN-93 derail the ability of AKAP79 to efficiently recruit PKC for regulation of GluA1. Thus, AKAP79 endows PKC with a pharmacological profile that overlaps with CaMKII.
Figures

References
-
- Tokumitsu H., Chijiwa T., Hagiwara M., Mizutani A., Terasawa M., Hidaka H. (1990) J. Biol. Chem. 265, 4315–4320 - PubMed
-
- Sumi M., Kiuchi K., Ishikawa T., Ishii A., Hagiwara M., Nagatsu T., Hidaka H. (1991) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 181, 968–975 - PubMed
-
- Humphreys B. D., Virginio C., Surprenant A., Rice J., Dubyak G. R. (1998) Mol. Pharmacol. 54, 22–32 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

