Through a glass darkly: salt transport by the distal tubule
- PMID: 21157456
- PMCID: PMC3729292
- DOI: 10.1038/ki.2010.400
Through a glass darkly: salt transport by the distal tubule
Abstract
The distal convoluted tubule (DCT) plays a central role in blood pressure and potassium homeostasis, as evidenced by diseases that occur when its function is modified. The paper by van der Lubbe and colleagues makes clear that angiotensin II itself increases the activity and abundance of the thiazide-sensitive Na-Cl cotransporter (NCC), independent of changes in circulating aldosterone. This Commentary provides additional perspective on that work.
Figures
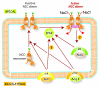
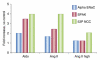
Comment on
-
Angiotensin II induces phosphorylation of the thiazide-sensitive sodium chloride cotransporter independent of aldosterone.Kidney Int. 2011 Jan;79(1):66-76. doi: 10.1038/ki.2010.290. Epub 2010 Aug 18. Kidney Int. 2011. PMID: 20720527
References
-
- Koeppen BM, Stanton BA. Sodium chloride transport: Distal Nephron. In: Seldin DW, Giebisch G, editors. The Kidney: Physiology and Pathophysiology. 2 edn Raven Press; New York: 1992. pp. 2003–2040.
-
- Velazquez H, Bartiss A, Bernstein P, et al. Adrenal steroids stimulate thiazide-sensitive NaCl transport by rat renal distal tubules. The American journal of physiology. 1996;270:F211–219. - PubMed
-
- Ecelbarger CA, Kim G-H, Terris J, et al. Vasopressin-mediated regulation of epithelial sodium channel abundance in rat kidney. AmJPhysiol Renal Physiol. 2000;279:F46–F53. - PubMed
-
- Bostanjoglo M, Reeves WB, Reilly RF, et al. 11Beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase, mineralocorticoid receptor, and thiazide-sensitive Na-Cl cotransporter expression by distal tubules. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1998;9:1347–1358. - PubMed
-
- Mutig K, Paliege A, Kahl T, et al. Vasopressin V2 receptor expression along rat, mouse, and human renal epithelia with focus on TAL. American journal of physiology. 2007;293:F1166–1177. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

