The Hyb hydrogenase permits hydrogen-dependent respiratory growth of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium
- PMID: 21157514
- PMCID: PMC3000549
- DOI: 10.1128/mBio.00284-10
The Hyb hydrogenase permits hydrogen-dependent respiratory growth of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium
Abstract
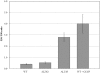
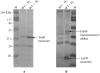
Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium contains three distinct respiratory hydrogenases, all of which contribute to virulence. Addition of H(2) significantly enhanced the growth rate and yield of S. Typhimurium in an amino acid-containing medium; this occurred with three different terminal respiratory electron acceptors. Based on studies with site-specific double-hydrogenase mutant strains, most of this H(2)-dependent growth increase was attributed to the Hyb hydrogenase, rather than to the Hya or Hyd respiratory H(2)-oxidizing enzymes. The wild type strain with H(2) had 4.0-fold greater uptake of (14)C-labeled amino acids over a period of minutes than did cells incubated without H(2). The double-uptake hydrogenase mutant containing only the Hyb hydrogenase transported amino acids H(2) dependently like the wild type. The Hyb-only-containing strain produced a membrane potential comparable to that of the wild type. The H(2)-stimulated amino acid uptake of the wild type and the Hyb-only strain was inhibited by the protonophore carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazone but was less affected by the ATP synthase inhibitor sodium orthovanadate. In the wild type, proteins TonB and ExbD, which are known to couple proton motive force (PMF) to transport processes, were induced by H(2) exposure, as were the genes corresponding to these periplasmic PMF-coupling factors. However, studies on tonB and exbD single mutant strains could not confirm a major role for these proteins in amino acid transport. The results link H(2) oxidation via the Hyb enzyme to growth, amino acid transport, and expression of periplasmic proteins that facilitate PMF-mediated transport across the outer membrane.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Respiratory hydrogen use by Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium is essential for virulence.Infect Immun. 2004 Nov;72(11):6294-9. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.11.6294-6299.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 15501756 Free PMC article.
-
Differential expression of NiFe uptake-type hydrogenase genes in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.Microbiology (Reading). 2007 Oct;153(Pt 10):3508-3516. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.2007/009027-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2007. PMID: 17906148
-
Role of the Hya hydrogenase in recycling of anaerobically produced H2 in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009 Mar;75(5):1456-9. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02064-08. Epub 2008 Dec 29. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19114523 Free PMC article.
-
Bioenergetic aspects of archaeal and bacterial hydrogen metabolism.Adv Microb Physiol. 2019;74:487-514. doi: 10.1016/bs.ampbs.2019.02.005. Epub 2019 Feb 28. Adv Microb Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31126536 Review.
-
Molecular Hydrogen Metabolism: a Widespread Trait of Pathogenic Bacteria and Protists.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2020 Jan 29;84(1):e00092-19. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00092-19. Print 2020 Feb 19. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2020. PMID: 31996394 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Edwardsiella tarda Sip2: A Serum-Induced Protein That Is Essential to Serum Survival, Acid Resistance, Intracellular Replication, and Host Infection.Front Microbiol. 2018 May 25;9:1084. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.01084. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29887847 Free PMC article.
-
Exploiting host immunity: the Salmonella paradigm.Trends Immunol. 2015 Feb;36(2):112-20. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2014.12.003. Epub 2015 Jan 9. Trends Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25582038 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nickel chelation therapy as an approach to combat multi-drug resistant enteric pathogens.Sci Rep. 2019 Sep 25;9(1):13851. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-50027-0. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31554822 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced Growth of Pilin-Deficient Geobacter sulfurreducens Mutants in Carbon Poor and Electron Donor Limiting Conditions.Microb Ecol. 2019 Oct;78(3):618-630. doi: 10.1007/s00248-019-01316-8. Epub 2019 Feb 13. Microb Ecol. 2019. PMID: 30759269
-
Neglected gut microbiome: interactions of the non-bacterial gut microbiota with enteric pathogens.Gut Microbes. 2023 Jan-Dec;15(1):2226916. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2023.2226916. Gut Microbes. 2023. PMID: 37365731 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Maier R. J. 2003. Availability and use of molecular hydrogen as an energy substrate for Helicobacter species. Microbes Infect. 5:1159–1163 - PubMed
-
- Russell J. B. 1998. The importance of pH in the regulation of ruminal acetate to propionate ratio and methane production in vitro. J. Dairy Sci. 81:3222–3230 - PubMed
-
- Marthinsen D., Fleming S. E. 1982. Excretion of breath and flatus gases by humans consuming high-fiber diets. J. Nutr. 112:1133–1143 - PubMed
-
- Levitt M. D., Hirsh P., Fetzer C. A., Sheahan M., Levine A. S. 1987. H2 excretion after ingestion of complex carbohydrates. Gastroenterology 92:383–389 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
