Alpha-Tocopherol Modulates Transcriptional Activities that Affect Essential Biological Processes in Bovine Cells
- PMID: 21157515
- PMCID: PMC3001320
- DOI: 10.4137/GRSB.S6007
Alpha-Tocopherol Modulates Transcriptional Activities that Affect Essential Biological Processes in Bovine Cells
Abstract
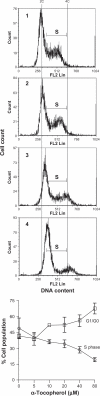
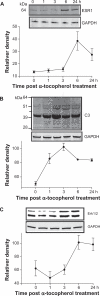
Using global expression profiling and pathway analysis on α-tocopherol-induced gene perturbation in bovine cells, this study has generated comprehensive information on the physiological functions of α-tocopherol. The data confirmed α-tocopherol is a potent regulator of gene expression and α-tocopherol possesses novel transcriptional activities that affect essential biological processes. The genes identified fall within a broad range of functional categories and provide the molecular basis for its distinctive effects. Enrichment analyses of gene regulatory networks indicate α-tocopherol alter the canonical pathway of lipid metabolism and transcription factors SREBP1 and SREBP2, (Sterol regulatory element binding proteins), which mediate the regulatory functions of lipid metabolism. Transcription factors HNF4-α (Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4), c-Myc, SP1 (Sp1 transcription factor), ESR1 (estrogen receptor 1, nuclear), and androgen receptor, along with several others, were centered as the hubs of transcription regulation networks. The data also provided direct evidence that α-tocopherol is involved in maintaining immuno-homeostasis through targeting the C3 (Complement Component 3) gene.
Keywords: ESR1; bovine cells; gene regulation; lipid metabolism; α-tocopherol.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Alpha-Tocopherol Alters Transcription Activities that Modulates Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha (TNF-α) Induced Inflammatory Response in Bovine Cells.Gene Regul Syst Bio. 2012;6:1-14. doi: 10.4137/GRSB.S8303. Epub 2011 Dec 5. Gene Regul Syst Bio. 2012. PMID: 22267916 Free PMC article.
-
Conservation of lipid metabolic gene transcriptional regulatory networks in fish and mammals.Gene. 2014 Jan 15;534(1):1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2013.10.040. Epub 2013 Oct 28. Gene. 2014. PMID: 24177230
-
Sex and circadian modulatory effects on rat liver as assessed by transcriptome analyses.J Toxicol Sci. 2011 Jan;36(1):9-22. doi: 10.2131/jts.36.9. J Toxicol Sci. 2011. PMID: 21297337
-
Transcriptional regulatory networks in lipid metabolism control ABCA1 expression.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005 Jun 15;1735(1):1-19. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2005.04.004. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005. PMID: 15922656 Review.
-
Non-antioxidant activities of vitamin E.Curr Med Chem. 2004 May;11(9):1113-33. doi: 10.2174/0929867043365332. Curr Med Chem. 2004. PMID: 15134510 Review.
Cited by
-
Antioxidant-independent activities of alpha-tocopherol.J Biol Chem. 2025 Apr;301(4):108327. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2025.108327. Epub 2025 Feb 18. J Biol Chem. 2025. PMID: 39978678 Free PMC article.
-
Role of vitamin E on bovine skeletal-muscle-derived cells from Korean native cattle under heat treatment.J Anim Sci. 2024 Jan 3;102:skae292. doi: 10.1093/jas/skae292. J Anim Sci. 2024. PMID: 39383093
-
Alpha-Tocopherol Alters Transcription Activities that Modulates Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha (TNF-α) Induced Inflammatory Response in Bovine Cells.Gene Regul Syst Bio. 2012;6:1-14. doi: 10.4137/GRSB.S8303. Epub 2011 Dec 5. Gene Regul Syst Bio. 2012. PMID: 22267916 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jensen SK, Lauridsen C. Alpha-tocopherol stereoisomers. Vitam Horm. 2007;76:281–308. - PubMed
-
- Prasad KN, Edwards-Prasad J. Effects of tocopherol (vitamin E) acid succinate on morphological alterations and growth inhibition in melanoma cells in culture. Cancer Res. 1982 Feb;42(2):550–5. - PubMed
-
- Prasad KN, Kumar B, Yan XD, Hanson AJ, Cole WC. Alpha-tocopheryl succinate, the most effective form of vitamin E for adjuvant cancer treatment: a review. J Am Coll Nutr. 2003 Apr;22(2):108–17. - PubMed
-
- Galli F, Azzi A. Present trends in vitamin E research. Biofactors. 2010 Jan;36(1):33–42. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

