Sphingosine-1-phosphate and immune regulation: trafficking and beyond
- PMID: 21159389
- PMCID: PMC3017656
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tips.2010.11.002
Sphingosine-1-phosphate and immune regulation: trafficking and beyond
Abstract
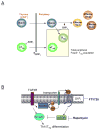
Sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) is a bioactive lipid with important functions in the immune system. S1P levels are regulated by the balance between its synthesis through sphingosine kinases and its degradation by S1P lyase. S1P signals through plasma membrane G-protein-coupled receptors (S1PR1-S1PR5) or acts directly on intracellular targets. Although it has long been known that the S1P-S1PR1 axis mediates T cell egress from lymphoid organs, recent studies have revealed intrinsic functions of S1P and its receptors in both innate and adaptive immune systems that are independent of immune cell trafficking. Here I summarize recent advances in understanding of the roles of S1P and S1P receptors in inflammatory and allergic responses and lymphocyte differentiation, which directly contribute to the regulation of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. I also describe strategies to target S1P and S1P receptors for immune-mediated diseases, particularly the immunosuppressant FTY720 (fingolimod), which has recently become the first oral therapy for relapsing multiple sclerosis.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

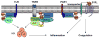
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

