Increased renal ENaC subunits and sodium retention in rats with chronic heart failure
- PMID: 21159737
- PMCID: PMC4068120
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00254.2010
Increased renal ENaC subunits and sodium retention in rats with chronic heart failure
Abstract
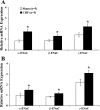
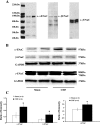
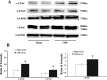
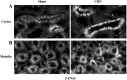
Renal tubular dysfunction could be involved in the increased sodium and water reabsorption in chronic heart failure (CHF). The goal of the present study was to examine the molecular basis for the increased renal sodium and water retention in CHF. We hypothesized that dysregulation of renal epithelial sodium channels (ENaC) could be involved in the pathogenesis of CHF. The left coronary ligation-induced model of heart failure in the rat was used. Real-time PCR and Western blot analysis indicated that the mRNA and protein abundance of α-, β-, and γ-subunits of ENaC were significantly increased by in the cortex (mRNA: α-ENaC Δ104 ± 24%, β-ENaC Δ47 ± 16%, γ-ENaC Δ55 ± 18%; protein: α-ENaC Δ114 ± 28%, β-ENaC Δ150 ± 31%, γ-ENaC Δ39 ± 5% compared with sham rats) and outer medulla (mRNA: α-ENaC Δ52 ± 18%, β-ENaC Δ38 ± 8%, γ-ENaC Δ39 ± 13%; protein: α-ENaC Δ88 ± 16%, β-ENaC Δ94 ± 28%, γ-ENaC Δ45 ± 9% compared with sham rats) of CHF compared with sham-operated rats. Immunohistochemistry microscopy confirmed the increased labeling of α-, β-, and γ-ENaC subunits in the collecting duct segments in rats with CHF. Furthermore, there was a significant increase in diuretic (7-fold compared with sham) and natriuretic responses (3-fold compared with sham) to ENaC inhibitor benzamil in the rats with CHF. Absence of renal nerves produced a greater contribution of ENaC in sodium retention in rats with CHF. These results suggest that the increased expression of renal ENaC subunits may contribute to the renal sodium and water retention observed during CHF.
Figures




Comment in
-
Clues to renal sodium retention.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2011 Mar;300(3):F639-40. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00737.2010. Epub 2011 Jan 12. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21228112 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Abildgaard U, Andersen JS, Daugaard G, Aldershvile J, Nielsen SL, Christensen NJ, Leyssac PP. Renal function in patients with untreated acute myocardial infarction. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 52: 689–695, 1992 - PubMed
-
- Beutler K, Masilamani S, Turban S, Nielsen J, Brooks HL, Ageloff S, Fenton RA, Packer RK, Knepper MA. Long-term regulation of ENaC expression in kidney by angiotensin II. Hypertension 41: 1143–1150, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Blazer-Yost BL, Liu X, Helman SI. Hormonal regulation of ENaCs: insulin and aldosterone. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 274: C1373–C1379, 1998 - PubMed
-
- Burrell LM, Risvanis J, Johnston CI, Naitoh M, Balding LC. Vasopressin receptor antagonism: a therapeutic option in heart failure and hypertension. Exp Physiol 85: 259S–265S, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Canessa CM, Shild L, Buell L, Thorens B, Gautschi I, Horisberger JD, Rossier BC. Amiloride-sensitive epithelial Na+ channel is made of three homologous subunits. Nature 367: 463–467, 1994 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

