Immunostimulatory activity of major membrane protein II from Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- PMID: 21159924
- PMCID: PMC3067359
- DOI: 10.1128/CVI.00459-10
Immunostimulatory activity of major membrane protein II from Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Abstract
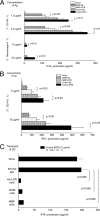
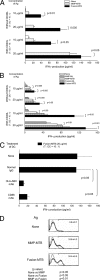
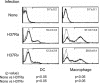
Previously, we observed that both major membrane protein II of Mycobacterium leprae (MMP-ML) and its fusion with M. bovis BCG (BCG)-derived heat shock protein 70 (HSP70) (Fusion-ML) are immunogenic and that recombinant BCG secreting either of these proteins effectively inhibits the multiplication of M. leprae in mice. Here, we purified M. tuberculosis-derived major membrane protein II (MMP-MTB) and its fusion with HSP70 (Fusion-MTB) in a lipopolysaccharide-free condition and evaluated their immunostimulatory abilities. Both MMP-MTB and Fusion-MTB activated monocyte-derived dendritic cells (DC) in terms of phenotype and interleukin-12 (IL-12) production, but Fusion-MTB more efficiently activated them than MMP-MTB did. The IL-12 production was a consequence of the ligation of those recombinant proteins with Toll-like receptor 2. The M. tuberculosis-derived and M. leprae-derived recombinant proteins activated naïve T cells of both CD4 and CD8 subsets, but M. tuberculosis-derived proteins were superior to M. leprae-derived proteins and fusion proteins were superior to MMP, regardless of the origin of the protein. Memory-type CD4(+) T cells obtained from BCG-vaccinated healthy individuals seem to be primed with MMP-MTB by the vaccination, and both M. tuberculosis-derived recombinant proteins produced perforin-producing CD8(+) T cells from memory-type CD8(+) T cells. Further, infection of DC and macrophages with M. tuberculosis H37Ra and H37Rv induced the expression of MMP on their surface. These results indicate that M. tuberculosis-derived MMP, as a sole protein or as part of a fusion protein, may be useful for developing new vaccinating agents against tuberculosis.
Figures


References
-
- Aagaard, C. S., T. T. K. T. Hoang, C. Vingsbo-Lundberg, J. Dietrich, and P. Andersen. 2009. Quality and vaccine efficacy of CD4+ T cell responses directed to dominant and subdominant epitopes in ESAT-6 from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Immunol. 183:2659-2668. - PubMed
-
- Andersen, P. 2007. Tuberculosis vaccines: an update. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 5:484-487. - PubMed
-
- Andersen, P., and T. M. Doherty. 2005. The success and failure of BCG: implications for a novel tuberculosis vaccine. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 3:656-662. - PubMed
-
- Bardarov, S., et al. 2002. Specialized transduction: an efficient method for generating marked and unmarked targeted gene disruptions in Mycobacterium tuberculosis, M. bovis BCG and M. smegmatis. Microbiology 148(Pt. 10):3007-3017. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

