Can we use imipenem and meropenem Vitek 2 MICs for detection of suspected KPC and other-carbapenemase producers among species of Enterobacteriaceae?
- PMID: 21159944
- PMCID: PMC3043475
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.01178-10
Can we use imipenem and meropenem Vitek 2 MICs for detection of suspected KPC and other-carbapenemase producers among species of Enterobacteriaceae?
Abstract
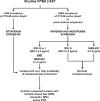
Imipenem and meropenem Vitek 2 MICs were evaluated for a panel of 104 Enterobacteriaceae for identification of carbapenemase producers. The sensitivity and specificity values for the new CLSI interpretative criteria (CLSI document M100-S20-U, 2010) were 98% and 83% for imipenem and 76% and 83% for meropenem, respectively. We propose an algorithm that is highly sensitive (98%) and specific (94%) for carbapenemase screening based on the combined use of imipenem and meropenem MICs.
Figures

References
-
- Boyd N. K., et al. 2009. Abstr. 49th Intersci. Conf. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., abstr. D-731/192
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

