Fragile X protein FMRP is required for homeostatic plasticity and regulation of synaptic strength by retinoic acid
- PMID: 21159962
- PMCID: PMC3073636
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3660-10.2010
Fragile X protein FMRP is required for homeostatic plasticity and regulation of synaptic strength by retinoic acid
Abstract
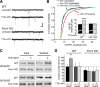
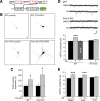
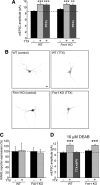
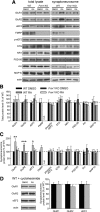
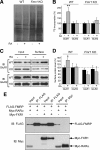
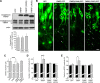
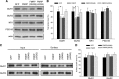
Homeostatic synaptic plasticity adjusts the strength of synapses during global changes in neural activity, thereby stabilizing the overall activity of neural networks. Suppression of synaptic activity increases synaptic strength by inducing synthesis of retinoic acid (RA), which activates postsynaptic synthesis of AMPA-type glutamate receptors (AMPARs) in dendrites and promotes synaptic insertion of newly synthesized AMPARs. Here, we show that fragile X mental retardation protein (FMRP), an RNA-binding protein that regulates dendritic protein synthesis, is essential for increases in synaptic strength induced by RA or by blockade of neural activity in the mouse hippocampus. Although activity-dependent RA synthesis is maintained in Fmr1 knock-out neurons, RA-dependent dendritic translation of GluR1-type AMPA receptors is impaired. Intriguingly, FMRP is only required for the form of homeostatic plasticity that is dependent on both RA signaling and local protein synthesis. Postsynaptic expression of wild-type or mutant FMRP(I304N) in knock-out neurons reduced the total, surface, and synaptic levels of AMPARs, implying a role for FMRP in regulating AMPAR abundance. Expression of FMRP lacking the RGG box RNA-binding domain had no effect on AMPAR levels. Importantly, postsynaptic expression of wild-type FMRP, but not FMRP(I304N) or FMRPΔRGG, restored synaptic scaling when expressed in knock-out neurons. Together, these findings identify an unanticipated role for FMRP in regulating homeostatic synaptic plasticity downstream of RA. Our results raise the possibility that at least some of the symptoms of fragile X syndrome reflect impaired homeostatic plasticity and impaired RA signaling.
Figures


Comment in
-
A fragile balance at synapses: new evidence supporting a role for FMRP in homeostatic plasticity.J Neurosci. 2011 May 4;31(18):6617-9. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0829-11.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21543589 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Ashley CT, Jr, Wilkinson KD, Reines D, Warren ST. FMR1 protein: conserved RNP family domains and selective RNA binding. Science. 1993;262:563–566. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
