Golgi cells operate as state-specific temporal filters at the input stage of the cerebellar cortex
- PMID: 21159970
- PMCID: PMC3073632
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3513-10.2010
Golgi cells operate as state-specific temporal filters at the input stage of the cerebellar cortex
Abstract
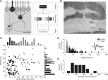
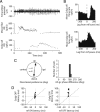
Cerebellar processing of incoming information begins at the synapse between mossy fibers and granule cells, a synapse that is strongly controlled through Golgi cell inhibition. Thus, Golgi cells are uniquely positioned to control the flow of information into the cerebellar cortex and understanding their responses during behavior is essential to understanding cerebellar function. Here we show, for the first time, that Golgi cells express a unique oculomotor-related signal that can be used to provide state- and time-specific filtering of granule cell activity. We used newly established criteria to identify the unique electrophysiological signature of Golgi cells and recorded these neurons in the squirrel monkey ventral paraflocculus during oculomotor behaviors. We found that they carry eye movement, but not vestibular or visual, information and that this eye movement information is only expressed within a specific range of eye positions for each neuron. In addition, simultaneous recordings of Golgi cells and nearby mossy fibers revealed that Golgi cells have the opposite directional tuning of the mossy fiber(s) that likely drive their responses, and that these responses are more sluggish than their mossy fiber counterparts. Because the mossy fiber inputs appear to convey the activity of burst-tonic neurons in the brainstem, Golgi cell responses reflect a time-filtered negative image of the motor command sent to the extraocular muscles. We suggest a role for Golgi cells in the construction of forward models of movement, commonly hypothesized as a major function of the cerebellar cortex in motor control.
Figures






References
-
- Chadderton P, Margrie TW, Häusser M. Integration of quanta in cerebellar granule cells during sensory processing. Nature. 2004;428:856–860. - PubMed
-
- Chan-Palay V, Palay SL. The synapse en marron between golgi II neurons and mossy fibers in the rat's cerebellar cortex. Z Anat Entwicklungsgesch. 1971;133:274–287. - PubMed
-
- D'Angelo E, De Zeeuw CI. Timing and plasticity in the cerebellum: focus on the granular layer. Trends Neurosci. 2009;32:30–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
