APOE4 allele disrupts resting state fMRI connectivity in the absence of amyloid plaques or decreased CSF Aβ42
- PMID: 21159973
- PMCID: PMC3023180
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3987-10.2010
APOE4 allele disrupts resting state fMRI connectivity in the absence of amyloid plaques or decreased CSF Aβ42
Abstract
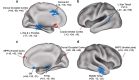
Identifying high-risk populations is an important component of disease prevention strategies. One approach for identifying at-risk populations for Alzheimer's disease (AD) is examining neuroimaging parameters that differ between patients, including functional connections known to be disrupted within the default-mode network. We have previously shown these same disruptions in cognitively normal elderly who have amyloid-β (Aβ) plaques [detected using Pittsburgh Compound B (PIB) PET imaging], suggesting neuronal toxicity of plaques. Here we sought to determine if pathological effects of apolipoprotein E ε4 (APOE4) genotype could be seen independent of Aβ plaque toxicity by examining resting state fMRI functional connectivity (fcMRI) in participants without preclinical fibrillar amyloid deposition (PIB-). Cognitively normal participants enrolled in longitudinal studies (n = 100, mean age = 62) who were PIB- were categorized into those with and without an APOE4 allele and studied using fcMRI. APOE4 allele carriers (E4+) differed significantly from E4- in functional connectivity of the precuneus to several regions previously defined as having abnormal connectivity in a group of AD participants. These effects were observed before any manifestations of cognitive changes and in the absence of brain fibrillar Aβ plaque deposition, suggesting that early manifestations of a genetic effect can be detected using fcMRI and that these changes may antedate the pathological effects of fibrillar amyloid plaque toxicity.
Figures

References
-
- Blennow K, de Leon MJ, Zetterberg H. Alzheimer's disease. Lancet. 2006;368:387–403. - PubMed
-
- Buckner RL, Snyder AZ, Shannon BJ, LaRossa G, Sachs R, Fotenos AF, Sheline YI, Klunk WE, Mathis CA, Morris JC, Mintun MA. Molecular, structural, and functional characterization of Alzheimer's disease: evidence for a relationship between default activity, amyloid, and memory. J Neurosci. 2005;25:7709–7717. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cairns NJ, Ikonomovic MD, Benzinger T, Storandt M, Fagan AM, Shah A, Reinwald LT, Carter D, Felton A, Holtzman DM, Mintun MA, Klunk WE, Morris JC. Absence of Pittsburgh Compound B detection of cerebral amyloid beta in a patient with clinical, cognitive, and cerebrospinal fluid markers of Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol. 2009;66:1557–1562. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Carmichael ST, Price JL. Connectional networks within the orbital and medial prefrontal cortex of macaque monkeys. J Comp Neurol. 1996;371:179–207. - PubMed
-
- Cirrito JR, Deane R, Fagan AM, Spinner ML, Parsadanian M, Finn MB, Jiang H, Prior JL, Sagare A, Bales KR, Paul SM, Zlokovic BV, Piwnica-Worms D, Holtzman DM. P-glycoprotein deficiency at the blood–brain barrier increases amyloid-beta deposition in an Alzheimer disease mouse model. J Clin Invest. 2005;115:3285–3290. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
