Protection against or triggering of Type 1 diabetes? Different roles for viral infections
- PMID: 21162649
- PMCID: PMC3077770
- DOI: 10.1586/eci.10.91
Protection against or triggering of Type 1 diabetes? Different roles for viral infections
Abstract
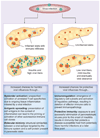
The emergence of autoreactivity that ultimately destroys insulin-producing β-cells and causes Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is a result of genetic susceptibility and environmental factors, such as viral infections. The ability to induce strong cellular immune responses and to cause inflammation in the target organ makes viral infections prime candidates for the initiation of islet autoreactivity. Indeed, certain viruses have been linked to the occurrence of T1D based on epidemiological, serological and histological findings; and several rodent studies clearly demonstrate that viral infections can trigger autoimmunity. However, viruses have also been shown to efficiently prevent autoimmunity, which underlines the beneficial aspects of exposure to microbial agents as suggested by the hygiene hypothesis. Here, we will try to untangle some aspects of the complex interplay between viruses and the immune system and we will recapitulate by what rationale certain viruses have been associated with T1D.
Figures
References
-
- Haller MJ, Atkinson MA, Schatz D. Type 1 diabetes mellitus: etiology, presentation, and management. Pediatr. Clin. North Am. 2005;52(6):1553–1578. - PubMed
-
- Variation and trends in incidence of childhood diabetes in Europe. EURODIAB ACE Study Group. Lancet. 2000;355(9207):873–876. - PubMed
-
- Patterson CC, Dahlquist GG, Gyurus E, Green A, Soltesz G. Incidence trends for childhood Type 1 diabetes in Europe during 1989–2003 and predicted new cases 2005–2020: a multicentre prospective registration study. Lancet. 2009;373(9680):2027–2033. - PubMed
Websites
-
- nPOD, Network for Pancreatic Organ Donors with Diabetes. www.jdrfnpod.org.
-
- TEDDY, The Environmental Determinants of Diabetes in the Young. http://teddy.epi.usf.edu.
-
- The Jackson Laboratory, Incidence study. http://type1diabetes.jax.org/gqc_ incidence_studies.html.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
