Development of targeted therapy for bladder cancer mediated by a double promoter plasmid expressing diphtheria toxin under the control of H19 and IGF2-P4 regulatory sequences
- PMID: 21162716
- PMCID: PMC3016259
- DOI: 10.1186/1479-5876-8-134
Development of targeted therapy for bladder cancer mediated by a double promoter plasmid expressing diphtheria toxin under the control of H19 and IGF2-P4 regulatory sequences
Abstract
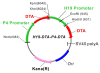
Background: The human IGF2-P4 and H19 promoters are highly active in a variety of human cancers (including bladder cancer), while existing at a nearly undetectable level in the surrounding normal tissue.Single promoter vectors expressing diphtheria toxin A-fragment (DTA) under the control regulation of IGF2-P4 or H19 regulatory sequences (IGF2-P4-DTA and H19-DTA) were previously successfully used in cell lines, animal models and recently in human patients with superficial cell carcinoma of the bladder (treated with H19-DTA). However this targeted medicine approach could be limited, as not all cancer patients express high levels of H19. Hence, a double promoter DTA-expressing vector was created, carrying on a single construct two separate genes expressing the diphtheria toxin A-fragment (DTA), from two different regulatory sequences, selected from the cancer-specific promoters H19 and IGF2-P4.
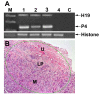
Methods: H19 and IGF2-P4 gene expression was tested in samples of Transitional Cell Carcinoma (TCC) of the bladder by in-situ hybridization (ISH) and by quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR). The therapeutic potential of the double promoter toxin vector H19-DTA-IGF2-P4-DTA was tested in TCC cell lines and in heterotopic and orthotopic animal models of bladder cancer.
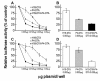
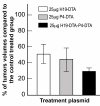
Results: Nearly 100% of TCC patients highly expressed IGF2-P4 and H19, as determined by ISH and by qRT-PCR. The double promoter vector exhibited superior tumor growth inhibition activity compared to the single promoter expression vectors, in cell lines and in heterotopic and orthotopic bladder tumors.
Conclusions: Our findings show that bladder tumors may be successfully treated by intravesical instillation of the double promoter vector H19-DTA-P4-DTA.Overall, the double promoter vector exhibited enhanced anti-cancer activity relative to single promoter expression vectors carrying either gene alone.
Figures








References
-
- Marston LW, Zbar B, Leach F, Cordon-Cardo C, Issacs W. In: Cancer: Principles & practice of oncology. VTDeVita, SHellman, SARosenberg, editor. Philadelppia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2001. Cancer of the genitourinary system; pp. 1343–1489.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

