Peak oxygen uptake in relation to total heart volume discriminates heart failure patients from healthy volunteers and athletes
- PMID: 21162743
- PMCID: PMC3022802
- DOI: 10.1186/1532-429X-12-74
Peak oxygen uptake in relation to total heart volume discriminates heart failure patients from healthy volunteers and athletes
Abstract
Background: An early sign of heart failure (HF) is a decreased cardiac reserve or inability to adequately increase cardiac output during exercise. Under normal circumstances maximal cardiac output is closely related to peak oxygen uptake (VO2peak) which has previously been shown to be closely related to total heart volume (THV). Thus, the aim of this study was to derive a VO2peak/THV ratio and to test the hypothesis that this ratio can be used to distinguish patients with HF from healthy volunteers and endurance athletes. Thirty-one patients with HF of different etiologies were retrospectively included and 131 control subjects (60 healthy volunteers and 71 athletes) were prospectively enrolled. Peak oxygen uptake was determined by maximal exercise test and THV was determined by cardiovascular magnetic resonance. The VO2peak/THV ratio was then derived and tested.
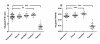
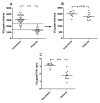
Results: Peak oxygen uptake was strongly correlated to THV (r2 = 0.74, p < 0.001) in the control subjects, but not for the patients (r2 = 0.0002, p = 0.95). The VO2peak/THV ratio differed significantly between control subjects and patients, even in patients with normal ejection fraction and after normalizing for hemoglobin levels (p < 0.001). In a multivariate analysis the VO2peak/THV ratio was the only independent predictor of presence of HF (p < 0.001).
Conclusions: The VO2peak/THV ratio can be used to distinguish patients with clinically diagnosed HF from healthy volunteers and athletes, even in patients with preserved systolic left ventricular function and after normalizing for hemoglobin levels.
Figures

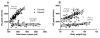
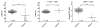
References
-
- Dickstein K, Cohen-Solal A, Filippatos G, McMurray JJ, Ponikowski P, Poole-Wilson PA, Stromberg A, van Veldhuisen DJ, Atar D, Hoes AW, Keren A, Mebazaa A, Nieminen M, Priori SG, Swedberg K, Vahanian A, Camm J, De Caterina R, Dean V, Dickstein K, Filippatos G, Funck-Brentano C, Hellemans I, Kristensen SD, McGregor K, Sechtem U, Silber S, Tendera M, Widimsky P, Zamorano JL. ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure 2008: the Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute and Chronic Heart Failure 2008 of the European Society of Cardiology. Developed in collaboration with the Heart Failure Association of the ESC (HFA) and endorsed by the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine (ESICM) Eur Heart J. 2008;29(19):2388–442. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehn309. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wheeldon NM, MacDonald TM, Flucker CJ, McKendrick AD, McDevitt DG, Struthers AD. Echocardiography in chronic heart failure in the community. Q J Med. 1993;86(1):17–23. - PubMed
-
- Hunt SA. ACC/AHA 2005 guideline update for the diagnosis and management of chronic heart failure in the adult: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (Writing Committee to Update the 2001 Guidelines for the Evaluation and Management of Heart Failure) J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005;46(6):e1–82. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2005.08.022. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ekblom B, Hermansen L. Cardiac output in athletes. J Appl Physiol. 1968;25(5):619–25. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

