Optimized method for the synthesis and purification of adenosine--folic acid conjugates for use as transcription initiators in the preparation of modified RNA
- PMID: 21163352
- PMCID: PMC3090705
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2010.12.007
Optimized method for the synthesis and purification of adenosine--folic acid conjugates for use as transcription initiators in the preparation of modified RNA
Abstract
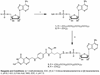
We present an optimized synthetic strategy for the attachment of molecules to 5'-adenosine monophosphate (AMP), which can then be used to label the 5'-end of RNA by T7 RNA polymerase mediated in vitro transcription. Through the use of a boronate affinity gel, we have developed an efficient route to the preparation of folate conjugated AMP with high yields and purity. Affi-Gel boronate is an affinity resin that selectively binds nucleoside and nucleoside derivatives at pH>7.5 and releases them at pH<6.5. This resin is used to efficiently bind and purify ribonucleotides such as AMP. This allows for the addition of a large excess of reactants and reagents in order to drive the reaction to completion and then allow easy purification without HPLC. The synthesis can be successfully scaled up to produce large quantities of AMP conjugates.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures






References
-
- Jeong JH, Mok H, Oh YK, Park TG. Bioconjug Chem. 2009;20:5–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

