Deconvolution of sinusoidal rapid EPR scans
- PMID: 21163677
- PMCID: PMC3097533
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmr.2010.11.015
Deconvolution of sinusoidal rapid EPR scans
Abstract
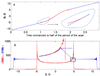
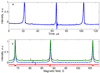
In rapid scan EPR the magnetic field is scanned through the signal in a time that is short relative to electron spin relaxation times. Previously it was shown that the slow-scan lineshape could be recovered from triangular rapid scans by Fourier deconvolution. In this paper a general Fourier deconvolution method is described and demonstrated to recover the slow-scan lineshape from sinusoidal rapid scans. Since an analytical expression for the Fourier transform of the driving function for a sinusoidal scan was not readily apparent, a numerical method was developed to do the deconvolution. The slow scan EPR lineshapes recovered from rapid triangular and sinusoidal scans are in excellent agreement for lithium phthalocyanine, a trityl radical, and the nitroxyl radical, tempone. The availability of a method to deconvolute sinusoidal rapid scans makes it possible to scan faster than is feasible for triangular scans because of hardware limitations on triangular scans.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Gupta RK, Ferretti JA, Becker ED. Rapid scan Fourier transform NMR spectroscopy. J. Magn. Reson. 1974;13:275–290.
-
- Dadok J, Sprecher RF. Correlation NMR spectroscopy. J. Magn. Reson. 1974;13:243–248.
-
- Winter J. Spin Resonance of Conduction Electrons, Magnetic Resonance in Metals. Oxford: Clarendon Press; 1971. pp. 155–156.
-
- Joshi JP, Ballard JR, Rinard GA, Quine RW, Eaton SS, Eaton GR. Rapid-Scan EPR with Triangular Scans and Fourier Deconvolution to Recover the Slow-Scan Spectrum. J. Magn. Reson. 2005;175:44–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

