Cystatin C identifies chronic kidney disease patients at higher risk for complications
- PMID: 21164029
- PMCID: PMC3014043
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2010050483
Cystatin C identifies chronic kidney disease patients at higher risk for complications
Abstract
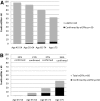
Although cystatin C is a stronger predictor of clinical outcomes associated with CKD than creatinine, the clinical role for cystatin C is unclear. We included 11,909 participants from the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA) and the Cardiovascular Health Study (CHS) and assessed risks for death, cardiovascular events, heart failure, and ESRD among persons categorized into mutually exclusive groups on the basis of the biomarkers that supported a diagnosis of CKD (eGFR <60 ml/min per 1.73 m(2)): creatinine only, cystatin C only, both, or neither. We used CKD-EPI equations to estimate GFR from these biomarkers. In MESA, 9% had CKD by the creatinine-based equation only, 2% had CKD by the cystatin C-based equation only, and 4% had CKD by both equations; in CHS, these percentages were 12, 4, and 13%, respectively. Compared with those without CKD, the adjusted hazard ratios (HR) for mortality in MESA were: 0.80 (95% CI 0.50 to 1.26) for CKD by creatinine only; 3.23 (95% CI 1.84 to 5.67) for CKD by cystatin C only; and 1.93 (95% CI 1.27 to 2.92) for CKD by both; in CHS, the adjusted HR were 1.09 (95% CI 0.98 to 1.21), 1.78 (95% CI 1.53 to 2.08), and 1.74 (95% CI 1.58 to 1.93), respectively. The pattern was similar for cardiovascular disease (CVD), heart failure, and kidney failure outcomes. In conclusion, among adults diagnosed with CKD using the creatinine-based CKD-EPI equation, the adverse prognosis is limited to the subset who also have CKD according to the cystatin C-based equation. Cystatin C may have a role in identifying persons with CKD who have the highest risk for complications.
Figures

Comment in
-
Is cystatin C the answer to detecting progression in CKD?J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011 Jan;22(1):9-11. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2010111189. Epub 2010 Dec 16. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011. PMID: 21164024 No abstract available.
References
-
- Coresh J, Selvin E, Stevens LA, Manzi J, Kusek JW, Eggers P, Van Lente F, Levey AS: Prevalence of chronic kidney disease in the United States. JAMA 298: 2038–2047, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Go AS, Chertow GM, Fan D, McCulloch CE, Hsu CY: Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N Engl J Med 351: 1296–1305, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Weiner DE, Tighiouart H, Amin MG, Stark PC, MacLeod B, Griffith JL, Salem DN, Levey AS, Sarnak MJ: Chronic kidney disease as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality: A pooled analysis of community-based studies. J Am Soc Nephrol 15: 1307–1315, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Fried LF, Biggs ML, Shlipak MG, Seliger S, Kestenbaum B, Stehman-Breen C, Sarnak M, Siscovick D, Harris T, Cauley J, Newman AB, Robbins J: Association of kidney function with incident hip fracture in older adults. J Am Soc Nephrol 18: 282–286, 2007 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- N01-HC-95162/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85085/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL080295/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095169/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85081/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95159/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95165/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85082/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK066488/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC-45133/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 1K23DK082793-01/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC075150/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095165/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85084/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95163/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085086/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85086/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095159/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K23 DK082793/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC-55222/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055222/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95164/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085079/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85083/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC-75150/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85080/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95160/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-85079/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-95161/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

