Role of iron in brain injury after intraventricular hemorrhage
- PMID: 21164132
- PMCID: PMC3078056
- DOI: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.110.602755
Role of iron in brain injury after intraventricular hemorrhage
Abstract
Background and purpose: Intraventricular extension of hemorrhage is a predictor of poor outcome in intracerebral hemorrhage, and iron overload contributes to brain injury after intracerebral hemorrhage. The current study investigated the role of iron in ventricular dilatation and neuronal death in a rat model of intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH).
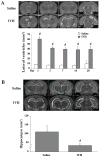
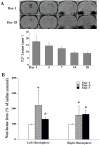
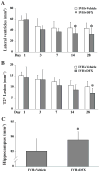
Methods: There were 2 parts in this study. First, male Sprague-Dawley rats had a 200-μL injection of either autologous blood or saline into the right lateral ventricle and were euthanized at different time points. Rats had MRI and brains were used for Western blot analysis, immunohistochemistry, histology, and brain tissue nonheme iron measurements. Second, rats had IVH and were treated with deferoxamine or vehicle, and rats were euthanized 4 weeks later for brain tissue loss and lateral ventricle size measurements.
Results: IVH resulted in brain iron accumulation, bilateral enlargement of the lateral ventricles, and hippocampal brain tissue loss. Iron accumulation was associated with upregulation of heme oxygenase-1 and ferritin. Systemic deferoxamine treatment reduced IVH-induced ventricular enlargement (eg, day 28: 32.7±10.6 vs 43.8±9.7 mm(3) in vehicle-treated group, n=8 to 9; P<0.05) and hippocampal brain tissue loss (hippocampal volume: 89.0±2.7 vs 85.2±4.1 mm(3) in the vehicle-treated group; P<0.05).
Conclusions: Iron has a role in brain injury after IVH. Deferoxamine may be a therapy for patients with IVH or intraventricular extension after intracerebral hemorrhage.
Figures



Comment in
-
Letter by Takeuchi and Nawashiro regarding article, "Role of iron in brain injury after intraventricular hemorrhage".Stroke. 2011 May;42(5):e378. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.613547. Epub 2011 Mar 17. Stroke. 2011. PMID: 21415402 No abstract available.
References
-
- Bhattathiri PS, Gregson B, Prasad KS, Mendelow AD. Intraventricular hemorrhage and hydrocephalus after spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: Results from the stich trial. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 2006;96:65–68. - PubMed
-
- Rosen D, Macdonald R, Huo D, Goldenberg F, Novakovic R, Frank J, Rosengart A. Intraventricular hemorrhage from ruptured aneurysm: Clinical characteristics, complications, and outcomes in a large, prospective, multicenter study population. Journal of Neurosurgery. 2007;107:261–265. - PubMed
-
- Xi G, Keep RF, Hoff JT. Mechanisms of brain injury after intracerebral hemorrhage. Lancet Neurol. 2006;5:53–63. - PubMed
-
- Nakamura T, Keep R, Hua Y, Schallert T, Hoff J, Xi G. Deferoxamine-induced attenuation of brain edema and neurological deficits in a rat model of intracerebral hemorrhage. J Neurosurg. 2004;100:672–678. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

