TRIM24 links a non-canonical histone signature to breast cancer
- PMID: 21164480
- PMCID: PMC3058826
- DOI: 10.1038/nature09542
TRIM24 links a non-canonical histone signature to breast cancer
Abstract
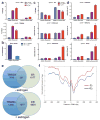
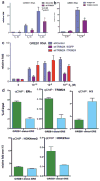
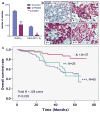
Recognition of modified histone species by distinct structural domains within 'reader' proteins plays a critical role in the regulation of gene expression. Readers that simultaneously recognize histones with multiple marks allow transduction of complex chromatin modification patterns into specific biological outcomes. Here we report that chromatin regulator tripartite motif-containing 24 (TRIM24) functions in humans as a reader of dual histone marks by means of tandem plant homeodomain (PHD) and bromodomain (Bromo) regions. The three-dimensional structure of the PHD-Bromo region of TRIM24 revealed a single functional unit for combinatorial recognition of unmodified H3K4 (that is, histone H3 unmodified at lysine 4, H3K4me0) and acetylated H3K23 (histone H3 acetylated at lysine 23, H3K23ac) within the same histone tail. TRIM24 binds chromatin and oestrogen receptor to activate oestrogen-dependent genes associated with cellular proliferation and tumour development. Aberrant expression of TRIM24 negatively correlates with survival of breast cancer patients. The PHD-Bromo of TRIM24 provides a structural rationale for chromatin activation through a non-canonical histone signature, establishing a new route by which chromatin readers may influence cancer pathogenesis.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

