Anti-apoptotic effect of hyperglycemia can allow survival of potentially autoreactive T cells
- PMID: 21164518
- PMCID: PMC3131907
- DOI: 10.1038/cdd.2010.163
Anti-apoptotic effect of hyperglycemia can allow survival of potentially autoreactive T cells
Erratum in
- Cell Death Differ. 2012 Nov;19(11):1892
Abstract
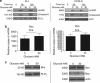
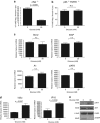
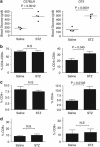
Thymocyte development is a tightly controlled multi-step process involving selective elimination of self-reactive and non-functional T cells by apoptosis. This developmental process depends on signaling by Notch, IL-7 and active glucose metabolism. In this study, we explored the requirement of glucose for thymocyte survival and found that in addition to metabolic regulation, glucose leads to the expression of anti-apoptotic genes. Under hyperglycemic conditions, both mouse and human thymocytes demonstrate enhanced survival. We show that glucose-induced anti-apoptotic genes are dependent on NF-κB p65 because high glucose is unable to attenuate normal ongoing apoptosis of thymocytes isolated from p65 knockout mice. Furthermore, we demonstrate that in vivo hyperglycemia decreases apoptosis of thymocytes allowing for survival of potentially self-reactive thymocytes. These results imply that hyperglycemic conditions could contribute to the development of autoimmunity through dysregulated thymic selection.
© 2011 Macmillan Publishers Limited
Figures



References
-
- Patterson CC, Dahlquist GG, Gyurus E, Green A, Soltesz G. Incidence trends for childhood type 1 diabetes in Europe during 1989–2003 and predicted new cases 2005–20: a multicentre prospective registration study. Lancet. 2009;373:2027–2033. - PubMed
-
- Ciofani M, Zuniga-Pflucker JC. Notch promotes survival of pre-T cells at the beta-selection checkpoint by regulating cellular metabolism. Nat Immunol. 2005;6:881–888. - PubMed
-
- Hayday AC, Pennington DJ. Key factors in the organized chaos of early T cell development. Nat Immunol. 2007;8:137–144. - PubMed
-
- Zhang N, Hartig H, Dzhagalov I, Draper D, He YW. The role of apoptosis in the development and function of T lymphocytes. Cell Res. 2005;15:749–769. - PubMed
-
- Greiner EF, Guppy M, Brand K. Glucose is essential for proliferation and the glycolytic enzyme induction that provokes a transition to glycolytic energy production. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:31484–31490. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

