Partition of environmental chemicals between maternal and fetal blood and tissues
- PMID: 21166449
- PMCID: PMC3031182
- DOI: 10.1021/es1019614
Partition of environmental chemicals between maternal and fetal blood and tissues
Abstract
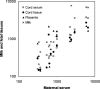
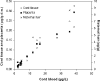
Passage of environmental chemicals across the placenta has important toxicological consequences, as well as for choosing samples for analysis and for interpreting the results. To obtain systematic data, we collected in 2000 maternal and cord blood, cord tissue, placenta, and milk in connection with births in the Faroe Islands, where exposures to marine contaminants is increased. In 15 sample sets, we measured a total of 87 environmental chemicals, almost all of which were detected both in maternal and fetal tissues. The maternal serum lipid-based concentrations of organohalogen compounds averaged 1.7 times those of cord serum, 2.8 times those of cord tissue and placenta, and 0.7 those of milk. For organohalogen compounds detectable in all matrices, a high degree of correlation between concentrations in maternal serum and the other tissues investigated was generally observed (r(2) > 0.5). Greater degree of chlorination resulted in lower transfer from maternal serum into milk. Concentrations of pentachlorbenzene, γ-hexachlorocyclohexane, and several polychlorinated biphenyl congeners with low chlorination were higher in fetal samples and showed poor correlation with maternal levels. Perfluorinated compounds occurred in lower concentrations in cord serum than in maternal serum. Cadmium, lead, mercury, and selenium were all detected in fetal samples, but only mercury showed close correlations among concentrations in different matrices. Although the environmental chemicals examined pass through the placenta and are excreted into milk, partitions between maternal and fetal samples are not uniform.
Figures

References
-
- Grandjean P.; Bellinger D.; Bergman A.; Cordier S.; Davey-Smith G.; Eskenazi B.; Gee D.; Gray K.; Hanson M.; van den Hazel P.; Heindel J. J.; Heinzow B.; Hertz-Picciotto I.; Hu H.; Huang T. T.; Jensen T. K.; Landrigan P. J.; McMillen I. C.; Murata K.; Ritz B.; Schoeters G.; Skakkebaek N. E.; Skerfving S.; Weihe P. The faroes statement: Human health effects of developmental exposure to chemicals in our environment. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2008, 102 (2), 73–75. - PubMed
-
- Andersen H. R.; Nielsen J. B.; Grandjean P. Toxicologic evidence of developmental neurotoxicity of environmental chemicals. Toxicology 2000, 144 (1−3), 121–127. - PubMed
-
- Grandjean P.; Brown S. S.; Reavey P.; Young D. S. Biomarkers of chemical exposure: State of the art. Clin. Chem. 1994, 40 (7B), 1360–1362. - PubMed
-
- Meijer L.; Weiss J.; Van Velzen M.; Brouwer A.; Bergman A.; Sauer P. J. Serum concentrations of neutral and phenolic organohalogens in pregnant women and some of their infants in The Netherlands. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42 (9), 3428–3433. - PubMed
-
- Nakamura T.; Nakai K.; Matsumura T.; Suzuki S.; Saito Y.; Satoh H. Determination of dioxins and polychlorinated biphenyls in breast milk, maternal blood and cord blood from residents of Tohoku, Japan. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 394 (1), 39–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

