The cardiovascular effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists
- PMID: 21167014
- PMCID: PMC3488299
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1755-5922.2010.00256.x
The cardiovascular effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists
Abstract
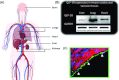
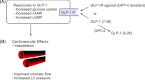
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R) agonists have been shown to regulate blood glucose concentrations by mechanisms including enhanced insulin synthesis/secretion, suppressed glucagon secretion, slowed gastric emptying, and enhanced satiety. GLP-1 receptors have also been identified in the heart, kidneys, and blood vessels, leading to the hypothesis that GLP-1R agonists may affect cardiovascular function or cardiovascular disease (CVD). The aim of this literature review was to assemble and assess preclinical and clinical data of potential medical importance regarding the cardiovascular effects of GLP-1R agonists. Preclinical studies with the GLP-1R agonists GLP-1, exenatide, or liraglutide provided evidence that GLP-1R stimulation favorably affects endothelial function, sodium excretion, recovery from ischemic injury, and myocardial function in animals. Similar observations have been made in exploratory studies on GLP-1 infusion in normal subjects and patients with type 2 diabetes. Post hoc analyses of phase III studies of patients with type 2 diabetes treated with exenatide(bid or qw) or liraglutide(qd) showed that these GLP-1R agonists reduced blood pressure, an effect largely independent of weight loss, and that liraglutide slightly increased heart rate. Preliminary data also indicated that GLP-1R agonists reduced markers of CVD risk such as C-reactive protein and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1. Ongoing studies are examining the effects of administering GLP-1R agonists to patients at risk of CVD, postangioplasty patients, post-CABG patients, and patients with heart failure. Additional studies should provide meaningful data to determine whether GLP-1R agonists provide unique treatment benefits to patients at risk for or with established CVD.
© 2010 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Emerging cardiovascular actions of the incretin hormone glucagon-like peptide-1: potential therapeutic benefits beyond glycaemic control?Br J Pharmacol. 2009 Aug;157(8):1340-51. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00376.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19681866 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beyond glucose lowering: glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists, body weight and the cardiovascular system.Diabetes Metab. 2011 Dec;37(6):477-88. doi: 10.1016/j.diabet.2011.07.001. Epub 2011 Aug 25. Diabetes Metab. 2011. PMID: 21871831 Review.
-
GLP-1 receptor agonists: a clinical perspective on cardiovascular effects.Diab Vasc Dis Res. 2012 Apr;9(2):95-108. doi: 10.1177/1479164112441526. Diab Vasc Dis Res. 2012. PMID: 22496442 Review.
-
Cardiovascular Actions and Clinical Outcomes With Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists and Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors.Circulation. 2017 Aug 29;136(9):849-870. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.028136. Circulation. 2017. PMID: 28847797 Review.
-
Impact of GLP-1 and GLP-1 receptor agonists on cardiovascular risk factors in type 2 diabetes.Curr Diabetes Rev. 2010 Jul;6(4):191-200. doi: 10.2174/157339910791658853. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2010. PMID: 20380625 Review.
Cited by
-
Cardiovascular Changes After Gastric Bypass Surgery: Involvement of Increased Secretions of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 and Brain Natriuretic Peptide.Obes Surg. 2015 Oct;25(10):1933-9. doi: 10.1007/s11695-015-1643-5. Obes Surg. 2015. PMID: 25788361
-
Combination therapy with GLP-1 receptor agonists and basal insulin: a systematic review of the literature.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2013 Jun;15(6):485-502. doi: 10.1111/dom.12025. Epub 2012 Nov 12. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2013. PMID: 23061470 Free PMC article.
-
[Exendin-4 alleviates diabetic cardiomyopathy in mice by regulating Sirt1/PGC1α].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2018 May 20;38(5):520-526. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4254.2018.05.03. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2018. PMID: 29891446 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Effects of exendin-4 and selenium on the expression of GLP-1R, IRS-1, and preproinsulin in the pancreas of diabetic rats.J Physiol Biochem. 2016 Aug;73(3):387-394. doi: 10.1007/s13105-017-0565-1. Epub 2017 Jun 7. J Physiol Biochem. 2016. PMID: 28589533
-
Myricetin: a potent approach for the treatment of type 2 diabetes as a natural class B GPCR agonist.FASEB J. 2017 Jun;31(6):2603-2611. doi: 10.1096/fj.201601339R. Epub 2017 Mar 7. FASEB J. 2017. PMID: 28270518 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amori RE, Lau J, Pittas AG. Efficacy and safety of incretin therapy in type 2 diabetes: Systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2007;298:194–206. [See the comment] - PubMed
-
- Drucker DJ, Nauck MA. The incretin system: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes. Lancet. 2006;368:1696–705. [See the comment] - PubMed
-
- Eeg-Olofsson K, Cederholm J, Nilsson PM, et al. Risk of cardiovascular disease and mortality in overweight and obese patients with type 2 diabetes: An observational study in 13,087 patients. Diabetologia. 2009;52:65–73. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

