The prevention of contrast induced nephropathy by sarpogrelate in patients with chronic kidney disease: a study protocol for a prospective randomized controlled clinical trial
- PMID: 21167080
- PMCID: PMC3018375
- DOI: 10.1186/1745-6215-11-122
The prevention of contrast induced nephropathy by sarpogrelate in patients with chronic kidney disease: a study protocol for a prospective randomized controlled clinical trial
Abstract
Background: Contrast-induced nephropathy (CIN) is a serious clinical problem associated with increased morbidity and mortality, particularly in patients with chronic renal insufficiency. Although some agents including hydration with saline are being prescribed to prevent renal deterioration in these high risk patients, their efficacy is not clearly defined and debatable. Therefore additional prophylactic pretreatments are needed.
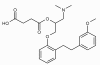
Methods/design: The present study aims to investigate differences in occurrence of CIN after sarpogrelate premedication in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD). 268 participants, aged 20-85 years with a clinical diagnosis of CKD will be recruited. They will be randomly allocated to one of two conditions: (i) routine treatment without sarpogrelate, and (ii) routine treatment with sarpogrelate (a fixed-flexible dose of 300 mg/day). The primary outcome is the occurrence of CIN during 4 weeks after receiving contrast agent.
Discussion: As of May 2010, there were no registered trials evaluating the therapeutic potentials of sarpogrelate in preventing for CIN. If sarpogrelate decreases the worsening of renal function and occurrence of CIN, it will provide a safe, easy and inexpensive treatment option.
Trial registration: NCT01165567.
Figures
References
-
- Gruberg L, Mintz GS, Mehran R, Gangas G, Lansky AJ, Kent KM, Pichard AD, Satler LF, Leon MB. The prognostic implications of further renal function deterioration within 48 h of interventional coronary procedures in patients with pre-existent chronic renal insufficiency. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2000;36:1542–1548. doi: 10.1016/S0735-1097(00)00917-7. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rudnick MR, Berns JS, Cohen RM, Goldfarb S. Contrast media-associated nephrotoxicity. Semin Nephrol. 1997;17:15–26. - PubMed
-
- Rihal CS, Textor SC, Grill DE, Berger PB, Ting HH, Best PJ, Singh M, Bell MR, Barsness GW, Mathew V, Garratt KN, Holmes DR Jr. Incidence and prognostic importance of acute renal failure after percutaneous coronary intervention. Circulation. 2002;105:2259–2264. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000016043.87291.33. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials