Multi-functional magnetic nanoparticles for magnetic resonance imaging and cancer therapy
- PMID: 21167595
- PMCID: PMC3021632
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.11.028
Multi-functional magnetic nanoparticles for magnetic resonance imaging and cancer therapy
Abstract
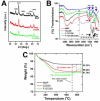
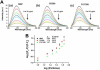
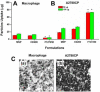
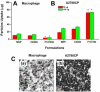
We have developed a multi-layer approach for the synthesis of water-dispersible superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for hyperthermia, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and drug delivery applications. In this approach, iron oxide core nanoparticles were obtained by precipitation of iron salts in the presence of ammonia and provided β-cyclodextrin and pluronic polymer (F127) coatings. This formulation (F127250) was highly water dispersible which allowed encapsulation of the anti-cancer drug(s) in β-cyclodextrin and pluronic polymer for sustained drug release. The F127250 formulation has exhibited superior hyperthermia effects over time under alternating magnetic field compared to pure magnetic nanoparticles (MNP) and β-cyclodextrin coated nanoparticles (CD200). Additionally, the improved MRI characteristics were also observed for the F127250 formulation in agar gel and in cisplatin resistant ovarian cancer cells (A12780CP) compared to MNP and CD200 formulations. Furthermore, the drug-loaded formulation of F127250 exhibited many folds of imaging contrast properties. Due to the internalization capacity of the F127250 formulation, its curcumin-loaded formulation (F127250-CUR) exhibited almost equivalent inhibition effects on A2780CP (ovarian), MDA-MB-231 (breast), and PC-3 (prostate) cancer cells even though curcumin release was only 40%. The improved therapeutic effects were verified by examining molecular effects using Western blotting and transmission electron microscopic (TEM) studies. F127250-CUR also exhibited haemocompatibility, suggesting a nanochemo-therapeutic agent for cancer therapy.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures








References
-
- Lu AH, Salabas EL, Schuth F. Magnetic nanoparticles: synthesis, protection, functionalization, and application. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2007;46:1222–44. - PubMed
-
- Ito A, Shinkai M, Honda H, Kobayashi T. Medical application of functionalized magnetic nanoparticles. J Biosci Bioeng. 2005;100:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Namdeo M, Saxena S, Tankhiwale R, Bajpai M, Mohan YM, Bajpai SK. Magnetic nanoparticles for drug delivery applications. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2008;8:3247–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

