A high proliferation rate is required for cell reprogramming and maintenance of human embryonic stem cell identity
- PMID: 21167714
- PMCID: PMC3034649
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2010.11.049
A high proliferation rate is required for cell reprogramming and maintenance of human embryonic stem cell identity
Abstract
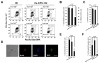
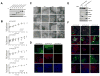
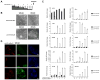
Human embryonic stem (hES) cells show an atypical cell-cycle regulation characterized by a high proliferation rate and a short G1 phase. In fact, a shortened G1 phase might protect ES cells from external signals inducing differentiation, as shown for certain stem cells. It has been suggested that self-renewal and pluripotency are intimately linked to cell-cycle regulation in ES cells, although little is known about the overall importance of the cell-cycle machinery in maintaining ES cell identity. An appealing model to address whether the acquisition of stem cell properties is linked to cell-cycle regulation emerged with the ability to generate induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells by expression of defined transcription factors. Here, we show that the characteristic cell-cycle signature of hES cells is acquired as an early event in cell reprogramming. We demonstrate that induction of cell proliferation increases reprogramming efficiency, whereas cell-cycle arrest inhibits successful reprogramming. Furthermore, we show that cell-cycle arrest is sufficient to drive hES cells toward irreversible differentiation. Our results establish a link that intertwines the mechanisms of cell-cycle control with the mechanisms underlying the acquisition and maintenance of ES cell identity.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- White J, Dalton S. Cell cycle control of embryonic stem cells. Stem Cell Rev. 2005;1:131–138. - PubMed
-
- Lange C, Huttner WB, Calegari F. Cdk4/cyclinD1 overexpression in neural stem cells shortens G1, delays neurogenesis, and promotes the generation and expansion of basal progenitors. Cell Stem Cell. 2009;5:320–31. - PubMed
-
- Zhang X, Neganova I, Przyborski S, Yang C, Cooke M, Atkinson SP, Anyfantis G, Fenyk S, Keith WN, Hoare SF, Hughes O, Strachan T, Stojkovic M, Hinds PW, Armstrong L, Lako M. A role for NANOG in G1 to S transition in human embryonic stem cells through direct binding of CDK6 and CDC25A. J Cell Biol. 2009;184:67–82. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

