Breaking the diffraction barrier: super-resolution imaging of cells
- PMID: 21168201
- PMCID: PMC3272504
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.12.002
Breaking the diffraction barrier: super-resolution imaging of cells
Abstract
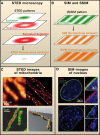
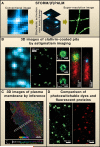
Anyone who has used a light microscope has wished that its resolution could be a little better. Now, after centuries of gradual improvements, fluorescence microscopy has made a quantum leap in its resolving power due, in large part, to advancements over the past several years in a new area of research called super-resolution fluorescence microscopy. In this Primer, we explain the principles of various super-resolution approaches, such as STED, (S)SIM, and STORM/(F)PALM. Then, we describe recent applications of super-resolution microscopy in cells, which demonstrate how these approaches are beginning to provide new insights into cell biology, microbiology, and neurobiology.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Abbe E. Beitrage zur Theorie des Mikroskops und der mikroskopischen Wahrnehmung. Arch. Mikroskop Anat. 1873;9:413–420.
-
- Betzig E, Patterson GH, Sougrat R, Lindwasser OW, Olenych S, Bonifacino JS, Davidson MW, Lippincott-Schwartz J, Hess HF. Imaging intracellular fluorescent proteins at nanometer resolution. Science. 2006;313:1642–1645. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

