Intra-operative 3D guidance and edema detection in prostate brachytherapy using a non-isocentric C-arm
- PMID: 21168357
- PMCID: PMC4695983
- DOI: 10.1016/j.media.2010.07.011
Intra-operative 3D guidance and edema detection in prostate brachytherapy using a non-isocentric C-arm
Abstract
Purpose: Brachytherapy (radioactive seed insertion) has emerged as one of the most effective treatment options for patients with prostate cancer, with the added benefit of a convenient outpatient procedure. The main limitation in contemporary brachytherapy is faulty seed placement, predominantly due to the presence of intra-operative edema (tissue expansion). Though currently not available, the capability to intra-operatively monitor the seed distribution, can make a significant improvement in cancer control. We present such a system here.
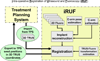
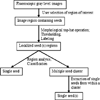
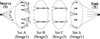
Methods: Intra-operative measurement of edema in prostate brachytherapy requires localization of inserted radioactive seeds relative to the prostate. Seeds were reconstructed using a typical non-isocentric C-arm, and exported to a commercial brachytherapy treatment planning system. Technical obstacles for 3D reconstruction on a non-isocentric C-arm include pose-dependent C-arm calibration; distortion correction; pose estimation of C-arm images; seed reconstruction; and C-arm to TRUS registration.
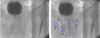
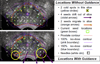
Results: In precision-machined hard phantoms with 40-100 seeds and soft tissue phantoms with 45-87 seeds, we correctly reconstructed the seed implant shape with an average 3D precision of 0.35 mm and 0.24 mm, respectively. In a DoD Phase-1 clinical trial on six patients with 48-82 planned seeds, we achieved intra-operative monitoring of seed distribution and dosimetry, correcting for dose inhomogeneities by inserting an average of over four additional seeds in the six enrolled patients (minimum 1; maximum 9). Additionally, in each patient, the system automatically detected intra-operative seed migration induced due to edema (mean 3.84 mm, STD 2.13 mm, Max 16.19 mm).
Conclusions: The proposed system is the first of a kind that makes intra-operative detection of edema (and subsequent re-optimization) possible on any typical non-isocentric C-arm, at negligible additional cost to the existing clinical installation. It achieves a significantly more homogeneous seed distribution, and has the potential to affect a paradigm shift in clinical practice. Large scale studies and commercialization are currently underway.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

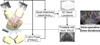









References
-
- Altschuler M, Kassaee A. Automated matching of corresponding seed images of three simulator radiographs to allow 3d triangulation of implanted seeds. Phys. Med. Biol. 1997;42(2):293–302. - PubMed
-
- Blasko J, Mate T, Sylvester J, Grimm P, Cavanagh W. Brachytherapy for carcinoma of the prostate: techniques, patient selection, and clinical outcomes. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2002;12(1):81–94. - PubMed
-
- Brunet-Benkhoucha M, Lassalle S, Béliveau-Nadeau D, Reniers B, Donath D, Taussky D, Carrier JF. Clinical implementation of a digital tomosynthesis-based seed reconstruction algorithm for intra-operative postimplant dose evaluation in low dose rate prostate brachytherapy. Med. Phys. 2009;36(11):5235–5544. - PubMed
-
- Cooperberg M, et al. The contemporary management of prostate cancer in the united states: lessons from the cancer of the prostate strategic urologic research endeavor (capsure), a national disease registry. J. Urol. 2004;171(4):1393–13401. - PubMed
-
- D’Amico A, et al. Real-time magnetic resonance imaging-guided brachytherapy in the treatment of selected patients with clinically localized prostate cancer. J. Endourol. 2000;14(4):367–370. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

