Intrinsic breast tumor subtypes, race, and long-term survival in the Carolina Breast Cancer Study
- PMID: 21169259
- PMCID: PMC3029098
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-1533
Intrinsic breast tumor subtypes, race, and long-term survival in the Carolina Breast Cancer Study
Abstract
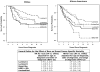
Purpose: Previous research identified differences in breast cancer-specific mortality across 4 intrinsic tumor subtypes: luminal A, luminal B, basal-like, and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 positive/estrogen receptor negative (HER2(+)/ER(-)).
Experimental design: We used immunohistochemical markers to subtype 1,149 invasive breast cancer patients (518 African American, 631 white) in the Carolina Breast Cancer Study, a population-based study of women diagnosed with breast cancer. Vital status was determined through 2006 using the National Death Index, with median follow-up of 9 years.
Results: Cancer subtypes luminal A, luminal B, basal-like, and HER2(+)/ER(-) were distributed as 64%, 11%, 11%, and 5% for whites, and 48%, 8%, 22%, and 7% for African Americans, respectively. Breast cancer mortality was higher for participants with HER2(+)/ER(-) and basal-like breast cancer compared with luminal A and B. African Americans had higher breast cancer-specific mortality than whites, but the effect of race was statistically significant only among women with luminal A breast cancer. However, when compared with the luminal A subtype within racial categories, mortality for participants with basal-like breast cancer was higher among whites (HR = 2.0, 95% CI: 1.2-3.4) than African Americans (HR = 1.5, 95% CI: 1.0-2.4), with the strongest effect seen in postmenopausal white women (HR = 3.9, 95% CI: 1.5-10.0).
Conclusions: Our results confirm the association of basal-like breast cancer with poor prognosis and suggest that basal-like breast cancer is not an inherently more aggressive disease in African American women compared with whites. Additional analyses are needed in populations with known treatment profiles to understand the role of tumor subtypes and race in breast cancer mortality, and in particular our finding that among women with luminal A breast cancer, African Americans have higher mortality than whites.
©2010 AACR.
Figures
Comment in
-
Toward a better understanding of race and cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2010 Dec 15;16(24):5920-2. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-2541. Clin Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 21169245
References
-
- Seer.cancer.gov [Internet] Bethesda: National Cancer Institute; [cited 2010 January 12]. Available from http://seer.cancer.gov.
-
- Carey LA, Perou CM, Livasy CA, et al. Race, breast cancer subtypes, and survival in the Carolina Breast Cancer Study. JAMA. 2006;295:2492–2502. - PubMed
-
- Lund MJ, Trivers KF, Porter PL, et al. Race and triple negative threats to breast cancer survival: a population-based study in Atlanta, GA. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2009;113:357–70. - PubMed
-
- Cheang MC, Voduc D, Bajdik C, et al. Basal-like breast cancer defined by five biomarkers has superior prognostic value than triple-negative phenotype. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:1368–76. - PubMed
-
- Yang XR, Sherman ME, Rimm DL, et al. Differences in risk factors for breast cancer molecular subtypes in a population-based study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2007;16:439–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous