A quantitative RNA code for mRNA target selection by the germline fate determinant GLD-1
- PMID: 21169991
- PMCID: PMC3034010
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2010.334
A quantitative RNA code for mRNA target selection by the germline fate determinant GLD-1
Abstract
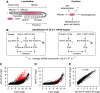
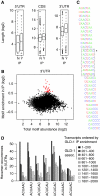
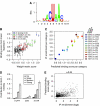
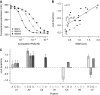
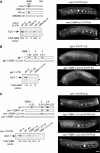
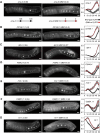
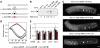
RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) are critical regulators of gene expression. To understand and predict the outcome of RBP-mediated regulation a comprehensive analysis of their interaction with RNA is necessary. The signal transduction and activation of RNA (STAR) family of RBPs includes developmental regulators and tumour suppressors such as Caenorhabditis elegans GLD-1, which is a key regulator of germ cell development. To obtain a comprehensive picture of GLD-1 interactions with the transcriptome, we identified GLD-1-associated mRNAs by RNA immunoprecipitation followed by microarray detection. Based on the computational analysis of these mRNAs we generated a predictive model, where GLD-1 association with mRNA is determined by the strength and number of 7-mer GLD-1-binding motifs (GBMs) within UTRs. We verified this quantitative model both in vitro, by competition GLD-1/GBM-binding experiments to determine relative affinity, and in vivo, by 'transplantation' experiments, where 'weak' and 'strong' GBMs imposed translational repression of increasing strength on a non-target mRNA. This study demonstrates that transcriptome-wide identification of RBP mRNA targets combined with quantitative computational analysis can generate highly predictive models of post-transcriptional regulatory networks.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Modeling the binding specificity of the RNA-binding protein GLD-1 suggests a function of coding region-located sites in translational repression.RNA. 2013 Oct;19(10):1317-26. doi: 10.1261/rna.037531.112. Epub 2013 Aug 23. RNA. 2013. PMID: 23974436 Free PMC article.
-
GLS-1, a novel P granule component, modulates a network of conserved RNA regulators to influence germ cell fate decisions.PLoS Genet. 2009 May;5(5):e1000494. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000494. Epub 2009 May 22. PLoS Genet. 2009. PMID: 19461891 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo and transcriptome-wide identification of RNA binding protein target sites.Mol Cell. 2011 Dec 9;44(5):828-40. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.11.009. Mol Cell. 2011. PMID: 22152485 Free PMC article.
-
C. elegans star proteins, GLD-1 and ASD-2, regulate specific RNA targets to control development.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010;693:106-22. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-7005-3_8. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2010. PMID: 21189689 Review.
-
RNA-binding proteins.WormBook. 2006 Apr 18:1-13. doi: 10.1895/wormbook.1.79.1. WormBook. 2006. PMID: 18050487 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The TRIM-NHL protein LIN-41 and the OMA RNA-binding proteins antagonistically control the prophase-to-metaphase transition and growth of Caenorhabditis elegans oocytes.Genetics. 2014 Dec;198(4):1535-58. doi: 10.1534/genetics.114.168831. Epub 2014 Sep 26. Genetics. 2014. PMID: 25261698 Free PMC article.
-
Translational activation maintains germline tissue homeostasis during adulthood.Worm. 2015 Jun 2;4(3):e1042644. doi: 10.1080/21624054.2015.1042644. eCollection 2015 Jul-Sep. Worm. 2015. PMID: 26430565 Free PMC article.
-
Transdifferentiation mediated tumor suppression by the endoplasmic reticulum stress sensor IRE-1 in C. elegans.Elife. 2015 Jul 20;4:e08005. doi: 10.7554/eLife.08005. Elife. 2015. PMID: 26192965 Free PMC article.
-
Solution structure of the QUA1 dimerization domain of pXqua, the Xenopus ortholog of Quaking.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e57345. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057345. Epub 2013 Mar 8. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23520467 Free PMC article.
-
Context-dependent function of a conserved translational regulatory module.Development. 2012 Apr;139(8):1509-21. doi: 10.1242/dev.070128. Epub 2012 Mar 7. Development. 2012. PMID: 22399679 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bailey TL, Elkan C (1994) Fitting a mixture model by expectation maximization to discover motifs in biopolymers. Proc Int Conf Intell Syst Mol Biol 2: 28–36 - PubMed
-
- Biedermann B, Hotz HR, Ciosk R (2010) The quaking family of RNA-binding proteins: coordinators of the cell cycle and differentiation. Cell Cycle 9: 1929–1933 - PubMed
-
- Biedermann B, Wright J, Senften M, Kalchhauser I, Sarathy G, Lee MH, Ciosk R (2009) Translational repression of cyclin E prevents precocious mitosis and embryonic gene activation during C. elegans meiosis. Dev Cell 17: 355–364 - PubMed
-
- Ciosk R, DePalma M, Priess JR (2006) Translational regulators maintain totipotency in the Caenorhabditis elegans germline. Science (New York, NY) 311: 851–853 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

