Doxorubicin causes diaphragm weakness in murine models of cancer chemotherapy
- PMID: 21171100
- PMCID: PMC3057655
- DOI: 10.1002/mus.21809
Doxorubicin causes diaphragm weakness in murine models of cancer chemotherapy
Abstract
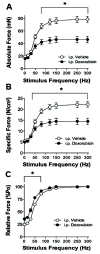
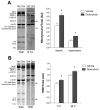
Doxorubicin is a chemotherapeutic agent prescribed for a variety of tumors. While undergoing treatment, patients exhibit frequent symptoms that suggest respiratory muscle weakness. Cancer patients can receive doxorubicin chemotherapy through either intravenous (IV) or intraperitoneal (IP) injections. We hypothesized that respiratory muscle function would be depressed in a murine model of chemotherapy. We tested this hypothesis by treating C57BL/6 mice with a clinical dose of doxorubicin (20 mg/kg) via IV or IP injection. Three days later we measured contractile properties of muscle fiber bundles isolated from the diaphragm. Doxorubicin consistently depressed diaphragm force with both methods of administration (P < 0.01). Doxorubicin IP exaggerated the depression in diaphragm force and stimulated tissue inflammation and muscle fiber injury. These results suggest that clinically relevant doses of doxorubicin cause respiratory muscle weakness and that the loss of function depends, in part, on the route of administration.
Copyright © 2010 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures




Similar articles
-
TNF/TNFR1 signaling mediates doxorubicin-induced diaphragm weakness.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2011 Feb;300(2):L225-31. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00264.2010. Epub 2010 Nov 19. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21097524 Free PMC article.
-
Interactive effects of corticosteroid and mechanical ventilation on diaphragm muscle function.Muscle Nerve. 2011 Jan;43(1):103-11. doi: 10.1002/mus.21821. Muscle Nerve. 2011. PMID: 21171101
-
Caspase activation contributes to endotoxin-induced diaphragm weakness.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2006 Jun;100(6):1770-7. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.01288.2005. Epub 2006 Feb 16. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2006. PMID: 16484358
-
Heart failure: HF-induced diaphragmatic atrophy and weakness.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2017 Jul;14(7):384. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2017.85. Epub 2017 Jun 1. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 28569270 Review. No abstract available.
-
Diaphragm contractile weakness due to reduced mechanical loading: role of titin.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2019 Aug 1;317(2):C167-C176. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00509.2018. Epub 2019 May 1. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31042425 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cancer- and Chemotherapy-Induced Musculoskeletal Degradation.JBMR Plus. 2019 Feb 25;3(3):e10187. doi: 10.1002/jbm4.10187. eCollection 2019 Mar. JBMR Plus. 2019. PMID: 30918923 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Docetaxel does not impair skeletal muscle force production in a murine model of cancer chemotherapy.Physiol Rep. 2017 Jun;5(11):e13261. doi: 10.14814/phy2.13261. Physiol Rep. 2017. PMID: 28583990 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of exercise and doxorubicin on acute diaphragm neuromuscular transmission failure.Exp Neurol. 2024 Aug;378:114818. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2024.114818. Epub 2024 May 21. Exp Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38782352 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Hyperbaric Oxygen Preconditioning on Doxorubicin Cardiorespiratory Toxicity.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Oct 20;11(10):2073. doi: 10.3390/antiox11102073. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36290796 Free PMC article.
-
Doxorubicin-induced skeletal muscle atrophy: Elucidating the underlying molecular pathways.Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2020 Jun;229(2):e13400. doi: 10.1111/apha.13400. Epub 2019 Oct 31. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2020. PMID: 31600860 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Elbl L, Vasova I, Tomaskova I, Jedlicka F, Kral Z, Navratil M, et al. Cardiopulmonary exercise testing in the evaluation of functional capacity after treatment of lymphomas in adults. Leuk Lymphoma. 2006;47:843–851. - PubMed
-
- Okuyama T, Akechi T, Kugaya A, Okamura H, Imoto S, Nakano T, et al. Factors correlated with fatigue in disease-free breast cancer patients: Application of the cancer fatigue scale. Support Care Cancer. 2000;8:215–222. - PubMed
-
- Hamilton AL, Killian KJ, Summers E, Jones NL. Muscle strength, symptom intensity, and exercise capacity in patients with cardiorespiratory disorders. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995;152:2021–2031. - PubMed
-
- Travers J, Dudgeon DJ, Amjadi K, McBride I, Dillon K, Laveneziana P, et al. Mechanisms of exertional dyspnea in patients with cancer. J Appl Physiol. 2008;104:57–66. - PubMed
-
- Chu E, DeNita VT. Physician’s cancer chemotherapy drug manual. Sudbury, Massachusetts: Jones & Bartlett Publishers, Inc.; 2008.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

