Depletion of nuclear actin is a key mediator of quiescence in epithelial cells
- PMID: 21172822
- PMCID: PMC3001411
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.073197
Depletion of nuclear actin is a key mediator of quiescence in epithelial cells
Abstract
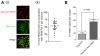
Functional differentiation is orchestrated by precise growth-regulatory controls conveyed by the tissue microenvironment. Cues from laminin 111 (LN1) lower transcription and suppress mammary epithelial cell growth in culture, but how LN1 induces quiescence is unknown. Recent literature points to involvement of nuclear β-actin in transcriptional regulation. Here, we show that quiescence induced by growth factor withdrawal, or LN1 addition, rapidly decreases nuclear β-actin. LN1, but not other extracellular matrix (ECM) molecules, decreases the levels of nuclear β-actin and destabilizes RNA polymerase (RNA Pol) II and III binding to transcription sites, leading to a dramatic drop in transcription and DNA synthesis. Constitutive overexpression of globular β-actin in the nucleus reverses the effect of LN1 on transcription and RNA Pol II association and prevents the cells from becoming quiescent in the presence of LN1. The physiological relevance of our findings was verified by identifying a clear spatial separation of LN1 and β-actin in developing mammary end buds. These data indicate a novel role for nuclear β-actin in growth arrest of epithelial cells and underscore the importance of the integrity of the basement membrane in homeostasis.
Figures
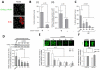
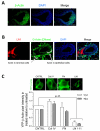
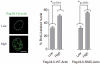
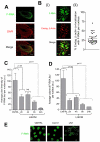
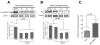

References
-
- Adolph S., Brusselbach S., Muller R. (1993). Inhibition of transcription blocks cell cycle progression of NIH3T3 fibroblasts specifically in G1. J. Cell Sci. 105, 113-122 - PubMed
-
- Andrin C., Hendzel M. J. (2004). F-actin-dependent insolubility of chromatin-modifying components. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 25017-25023 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01CA064786/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA064786/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54CA143836/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA126552/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA112970/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01CA143233/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA057621/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA057621/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA143233/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA064786/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54CA126552/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54CA112970/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CAPMC/ CIHR/Canada
- U54 CA143836/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

