A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial with the interleukin-1 receptor antagonist anakinra in patients with systemic-onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis (ANAJIS trial)
- PMID: 21173013
- PMCID: PMC3070271
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.2010.134254
A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial with the interleukin-1 receptor antagonist anakinra in patients with systemic-onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis (ANAJIS trial)
Abstract
Objectives: To assess the efficacy of the interleukin 1 receptor antagonist anakinra in systemic-onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis (SJIA).
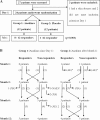
Methods: A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial was conducted. The primary objective was to compare the efficacy of a 1-month treatment with anakinra (2 mg/kg subcutaneous daily, maximum 100 mg) with a placebo between two groups each with 12 patients with SJIA. Response was defined by a 30% improvement of the paediatric American College of Rheumatology criteria for JIA, resolution of systemic symptoms and a decrease of at least 50% of both C-reactive protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rate compared with baseline. After month 1 (M1), patients taking placebo were switched to anakinra. Secondary objectives included tolerance and efficacy assessment for 12 months, and analyses of treatment effect on blood gene expression profiling.
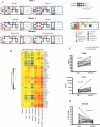
Results: At M1, 8/12 responders were receiving anakinra and 1 responder receiving placebo (p=0.003). Ten patients from the placebo group switched to anakinra; nine were responders at M2. Between M1 and M12, six patients stopped treatment owing to an adverse event (n=2), lack of efficacy (n=2) or a disease flare (n=2). Blood gene expression profiling at enrollment and at 6 months' follow-up showed one set of dysregulated genes that reverted to normal values in the clinical responders and a different set, including interferon (IFN)-inducible genes, that was induced by anakinra.
Conclusions: Anakinra treatment is effective in SJIA, at least in the short term. It is associated with normalisation of blood gene expression profiles in clinical responders and induces a de novo IFN signature.
Trial registration number: NCT00339157.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Petty RE, Southwood TR, Manners P, et al. International League of Associations for Rheumatology classification of juvenile idiopathic arthritis: second revision, Edmonton, 2001. J Rheumatol 2004;31:390–2 - PubMed
-
- Woo P, Southwood TR, Prieur AM, et al. Randomized, placebo-controlled, crossover trial of low-dose oral methotrexate in children with extended oligoarticular or systemic arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2000;43:1849–57 - PubMed
-
- Quartier P, Taupin P, Bourdeaut F, et al. Efficacy of etanercept for the treatment of juvenile idiopathic arthritis according to the onset type. Arthritis Rheum 2003;48:1093–101 - PubMed
-
- Yokota S, Imagawa T, Mori M, et al. Efficacy and safety of tocilizumab in patients with systemic-onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, withdrawal phase III trial. Lancet 2008;371:998–1006 - PubMed
-
- Spiegel LR, Schneider R, Lang BA, et al. Early predictors of poor functional outcome in systemic-onset juvenile rheumatoid arthritis: a multicenter cohort study. Arthritis Rheum 2000;43:2402–9 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

