Non-ATG-initiated translation directed by microsatellite expansions
- PMID: 21173221
- PMCID: PMC3017129
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1013343108
Non-ATG-initiated translation directed by microsatellite expansions
Abstract
Trinucleotide expansions cause disease by both protein- and RNA-mediated mechanisms. Unexpectedly, we discovered that CAG expansion constructs express homopolymeric polyglutamine, polyalanine, and polyserine proteins in the absence of an ATG start codon. This repeat-associated non-ATG translation (RAN translation) occurs across long, hairpin-forming repeats in transfected cells or when expansion constructs are integrated into the genome in lentiviral-transduced cells and brains. Additionally, we show that RAN translation across human spinocerebellar ataxia type 8 (SCA8) and myotonic dystrophy type 1 (DM1) CAG expansion transcripts results in the accumulation of SCA8 polyalanine and DM1 polyglutamine expansion proteins in previously established SCA8 and DM1 mouse models and human tissue. These results have implications for understanding fundamental mechanisms of gene expression. Moreover, these toxic, unexpected, homopolymeric proteins now should be considered in pathogenic models of microsatellite disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
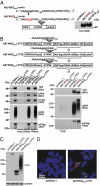
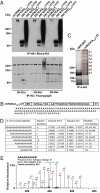
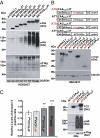

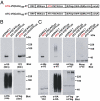
References
-
- Ranum LP, Cooper TA. RNA-mediated neuromuscular disorders. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2006;29:259–277. - PubMed
-
- Orr HT, Zoghbi HY. Trinucleotide repeat disorders. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2007;30:575–621. - PubMed
-
- Liquori CL, et al. Myotonic dystrophy type 2 caused by a CCTG expansion in intron 1 of ZNF9. Science. 2001;293:864–867. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

