Non-canonical NF-κB signaling pathway
- PMID: 21173796
- PMCID: PMC3193406
- DOI: 10.1038/cr.2010.177
Non-canonical NF-κB signaling pathway
Abstract
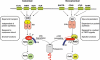
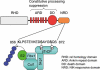
The non-canonical NF-κB pathway is an important arm of NF-κB signaling that predominantly targets activation of the p52/RelB NF-κB complex. This pathway depends on the inducible processing of p100, a molecule functioning as both the precursor of p52 and a RelB-specific inhibitor. A central signaling component of the non-canonical pathway is NF-κB-inducing kinase (NIK), which integrates signals from a subset of TNF receptor family members and activates a downstream kinase, IκB kinase-α (IKKα), for triggering p100 phosphorylation and processing. A unique mechanism of NIK regulation is through its fate control: the basal level of NIK is kept low by a TRAF-cIAP destruction complex and signal-induced non-canonical NF-κB signaling involves NIK stabilization. Tight control of the fate of NIK is important, since deregulated NIK accumulation is associated with lymphoid malignancies.
Figures

References
-
- Hayden MS, Ghosh S. Shared principles in NF-kappaB signaling. Cell. 2008;132:344–362. - PubMed
-
- Vallabhapurapu S, Karin M. Regulation and function of NF-kappaB transcription factors in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol. 2009;27:693–733. - PubMed
-
- Dejardin E. The alternative NF-kappaB pathway from biochemistry to biology: pitfalls and promises for future drug development. Biochem Pharmacol. 2006;72:1161–1179. - PubMed
-
- Xiao G, Harhaj EW, Sun SC. NF-kappaB-inducing kinase regulates the processing of NF-kappaB2 p100. Mol Cell. 2001;7:401–409. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

