Influenza vaccination coverage in the 2004/05, 2005/06, and 2006/07 seasons: a secondary data analysis based on billing data of the German associations of statutory health insurance physicians
- PMID: 21173931
- PMCID: PMC3004371
- DOI: 10.3238/arztebl.2010.0845
Influenza vaccination coverage in the 2004/05, 2005/06, and 2006/07 seasons: a secondary data analysis based on billing data of the German associations of statutory health insurance physicians
Abstract
Background: The German Standing Committee on Vaccination recommends annual vaccination for persons in high-risk groups in order to lower the disease burden associated with seasonal influenza. The stated target is 75% vaccination coverage of people over age 60 by the year 2010. We present statistics based on billing data of the German associations of statutory health insurance physicians regarding vaccination coverage for influenza in the three seasons from 2004/05 to 2006/07.
Methods: We analyzed anonymous data from 14 of the 17 associations of statutory health insurance physicians in Germany. The study population consisted of all persons covered by statutory health insurance in the geographical areas under study (61.5 million persons, or 86% of the total population of these areas). Vaccination coverage was calculated as the number of vaccinated persons divided by the number of persons covered by statutory health insurance.
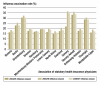
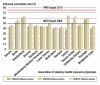
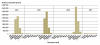
Results: The influenza vaccination coverage of the overall study population was 19% in 2004/05, 22% in 2005/06, and 21% in 2006/07. The coverage of persons over age 60 was 45% in 2004/05, 50% in 2005/06, and 49% in 2006/07 and was higher in areas that were formerly part of East Germany than in the rest of the country. More than a third of all vaccinated persons were vaccinated in all three seasons, as were almost half of the vaccinated persons over age 60.
Conclusion: There was no secular increase in influenza vaccination coverage over the period 2005/06 to 2006/07. The stated target of 75% vaccination coverage for persons over age 60 by the year 2010 would thus seem to represent a major challenge for all persons involved. The analysis of data of the associations of statutory health insurance physicians enables continuous monitoring of influenza vaccination coverage.
Figures
References
-
- Robert Koch-Institut. Survstat, http://www3rki.de/survstat, Datenstand. 2009. Aug 28,
-
- Buchholz U. Influenza-assoziierte Mortalität in Deutschland 1985-2006. Epid Bull. 2007;35:325–327.
-
- RKI. Empfehlungen der Ständigen Impfkommission (STIKO) am Robert Koch-Institut. Epid Bull. 2009;30:279–298.
-
- RKI. Auftakt der jährlichen Influenza-Impfaktion: Kommen Sie der Grippe zuvor. Jedes Jahr. Epid Bull. 2006;43
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

