Role of IKKα in skin squamous cell carcinomas
- PMID: 21174543
- PMCID: PMC7365019
- DOI: 10.2217/fon.10.166
Role of IKKα in skin squamous cell carcinomas
Abstract
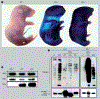
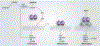
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) and basal cell carcinoma (BCC) are two major types of skin cancer derived from keratinocytes. SCC is a more aggressive type of cancer than BCC in humans. One significant difference between SCC and BCC is that SCC development is generally associated with cell dedifferentiation and morphological changes. When SCC is converted to spindle cell carcinoma, the latest stage of cancer, the tumor cells change to a fibroblastic cell morphology (epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition) and lose their differentiation markers. Recently, several laboratories have reported altered IκB kinase α (IKKα) protein localization, downregulated IKKα, and IKKα gene deletions and mutations in human SCCs of the skin, lung, esophagus, and neck and head. In addition, IKKα reduction promotes chemical carcinogen- and ultraviolet B-induced skin carcinogenesis, and IKKα deletion in keratinocytes causes spontaneous skin SCCs, but not BCCs, in mice. Thus, IKKα emerges as a bona fide skin tumor suppressor. In this article, we will discuss the role of IKKα in skin SCC development.
Figures
References
Bibliography
-
-
Mock BA, Connelly MA, McBride OW, Kozak CA, Marcu KB: CHUK, a conserved helix-lo op-helix ubiquitous kinase, maps to human chromosome 10 and mouse chromosome 19. Genomics 27,348–351 (1995).
■ Identifies the human conserved helix-loop-helix ubiquitous kinase (CHUK), IκBα kinase α (IKKα).
-
-
-
DiDonato JA, Hayakawa M, Rothwarf DM, Zandi E, Karin M: A cytokine-responsive IκB kinase that activates the transcription factor NF-κB. Nature 388, 548–554 (1997).
■ Identifies that IKKα phosphorylates IκBs.
-
-
- Mercurio F, Zhu H, Murray BW et al. : IKK-1 and IKK-2: cytokine-activated IκB kinases essential for NF-κB activation. Science 278, 860–866 (1997). - PubMed
-
- Rothwarf DM, Karin M: The NF-κB activation pathway: a paradigm in information transfer from membrane to nucleus. Sci. STKE 1999, RE1 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Karin M, Ben-Neriah Y: Phosphorylation meets ubiquitination: the control of NF-κB activity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 18, 621–663 (2000). - PubMed
Website
-
- National Cancer Institute. Cancer Genome Anatomy Project http://cgap.nci.nih.gov/Chromosomes/Mitelman
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
