Efficient generation and cryopreservation of cardiomyocytes derived from human embryonic stem cells
- PMID: 21175287
- PMCID: PMC3057133
- DOI: 10.2217/rme.10.91
Efficient generation and cryopreservation of cardiomyocytes derived from human embryonic stem cells
Abstract
Aim: Human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) represent a novel cell source to treat diseases such as heart failure and for use in drug screening. In this study, we aim to promote efficient generation of cardiomyocytes from hESCs by combining the current optimal techniques of controlled growth of undifferentiated cells and specific induction for cardiac differentiation. We also aim to examine whether these methods are scalable and whether the differentiated cells can be cryopreserved.
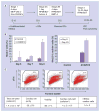
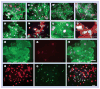
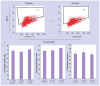
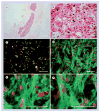
Methods & results: hESCs were maintained without conditioned medium or feeders and were sequentially treated with activin A and bone morphogenetic protein-4 in a serum-free medium. This led to differentiation into cell populations containing high percentages of cardiomyocytes. The differentiated cells expressed appropriate cardiomyocyte markers and maintained contractility in culture, and the majority of the cells displayed working chamber (atrial and ventricular) type electrophysiological properties. In addition, the cell growth and differentiation process was adaptable to large culture formats. Moreover, the cardiomyocytes survived following cryopreservation, and viable cardiac grafts were detected after transplantation of cryopreserved cells into rat hearts following myocardial infarctions.
Conclusion: These results demonstrate that cardiomyocytes of high quality can be efficiently generated and cryopreserved using hESCs maintained in serum-free medium, a step forward towards the application of these cells to human clinical use or drug discovery.
Figures



References
-
- Thomson JA, Itskovitz-Eldor J, Shapiro SS, et al. Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science. 1998;282:1145–1147. - PubMed
-
- Reubinoff BE, Pera MF, Fong CY, et al. Embryonic stem cell lines from human blastocysts: somatic differentiation in vitro. Nat Biotechnol. 2000;18(4):399–404. - PubMed
-
- Xue T, Cho HC, Akar FG, et al. Functional integration of electrically active cardiac derivatives from genetically engineered human embryonic stem cells with quiescent recipient ventricular cardiomyocytes: insights into the development of cell-based pacemakers. Circulation. 2005;111(1):11–20. - PubMed
-
- He JQ, Ma Y, Lee Y, et al. Human embryonic stem cells develop into multiple types of cardiac myocytes: action potential characterization. Circ Res. 2003;93(1):32–39. - PubMed
-
- Reppel M, Boettinger C, Hescheler J. β-adrenergic and muscarinic modulation of human embryonic stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2004;14(4–6):187–196. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
