The majority of total nuclear-encoded non-ribosomal RNA in a human cell is 'dark matter' un-annotated RNA
- PMID: 21176148
- PMCID: PMC3022773
- DOI: 10.1186/1741-7007-8-149
The majority of total nuclear-encoded non-ribosomal RNA in a human cell is 'dark matter' un-annotated RNA
Erratum in
- BMC Biol. 2011;9:86
Abstract
Background: Discovery that the transcriptional output of the human genome is far more complex than predicted by the current set of protein-coding annotations and that most RNAs produced do not appear to encode proteins has transformed our understanding of genome complexity and suggests new paradigms of genome regulation. However, the fraction of all cellular RNA whose function we do not understand and the fraction of the genome that is utilized to produce that RNA remain controversial. This is not simply a bookkeeping issue because the degree to which this un-annotated transcription is present has important implications with respect to its biologic function and to the general architecture of genome regulation. For example, efforts to elucidate how non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) regulate genome function will be compromised if that class of RNAs is dismissed as simply 'transcriptional noise'.
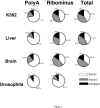
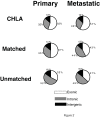
Results: We show that the relative mass of RNA whose function and/or structure we do not understand (the so called 'dark matter' RNAs), as a proportion of all non-ribosomal, non-mitochondrial human RNA (mt-RNA), can be greater than that of protein-encoding transcripts. This observation is obscured in studies that focus only on polyA-selected RNA, a method that enriches for protein coding RNAs and at the same time discards the vast majority of RNA prior to analysis. We further show the presence of a large number of very long, abundantly-transcribed regions (100's of kb) in intergenic space and further show that expression of these regions is associated with neoplastic transformation. These overlap some regions found previously in normal human embryonic tissues and raises an interesting hypothesis as to the function of these ncRNAs in both early development and neoplastic transformation.
Conclusions: We conclude that 'dark matter' RNA can constitute the majority of non-ribosomal, non-mitochondrial-RNA and a significant fraction arises from numerous very long, intergenic transcribed regions that could be involved in neoplastic transformation.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

