The reliability of toe systolic pressure and the toe brachial index in patients with diabetes
- PMID: 21176166
- PMCID: PMC3020155
- DOI: 10.1186/1757-1146-3-31
The reliability of toe systolic pressure and the toe brachial index in patients with diabetes
Abstract
Background: The Ankle Brachial Index is a useful clinical test for establishing blood supply to the foot. However, there are limitations to this method when conducted on people with diabetes. As an alternative to the Ankle Brachial Index, measuring Toe Systolic Pressures and the Toe Brachial Index have been recommended to assess the arterial blood supply to the foot. This study aimed to determine the intra and inter-rater reliability of the measurement of Toe Systolic Pressure and the Toe Brachial Index in patients with diabetes using a manual measurement system.
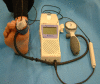
Methods: This was a repeated measures, reliability study. Three raters measured Toe Systolic Pressure and the Toe Brachial Index in thirty participants with diabetes. Measurement sessions occurred on two occasions, one week apart, using a manual photoplethysmography unit (Hadeco Smartdop 45) and a standardised measurement protocol.
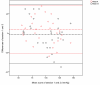
Results: The mean intra-class correlation for intra-rater reliability for toe systolic pressures was 0.87 (95% LOA: -25.97 to 26.06 mmHg) and the mean intra-class correlation for Toe Brachial Indices was 0.75 (95% LOA: -0.22 to 0.28). The intra-class correlation for inter-rater reliability was 0.88 for toe systolic pressures (95% LOA: -22.91 to 29.17.mmHg) and 0.77 for Toe Brachial Indices (95% LOA: -0.21 to 0.22).
Conclusion: Despite the reasonable intra-class correlation results, the range of error (95% LOA) was broad. This raises questions regarding the reliability of using a manual sphygmomanometer and PPG for the Toe Systolic Pressure and Toe Brachial Indice.
Figures

References
-
- Norman PE, Eikelboom JW, Hankey GJ. Peripheral arterial disease: prognostic significance and prevention of atherothrombotic complications. The Medical Journal of Australia. 2004;181(3):150–154. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

